Proposed underground geometry of the Mare Tranquillitatis on the Moon
Wagner and Robinson
A network of caves may be hidden just beneath the Moon's surface, and researchers may have finally discovered an access point. These caves have long been predicted, but until now it has been difficult to prove their existence or find a way to directly explore them with future missions.
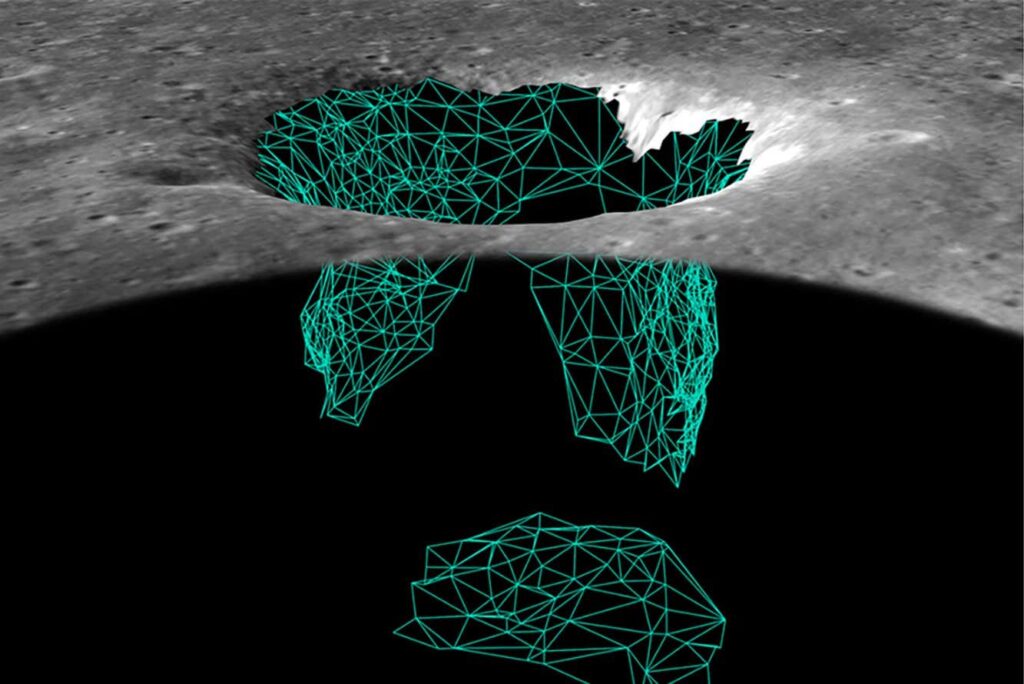
The Moon's surface is dotted with holes, or so-called skylights, which are openings in the ceilings of caves that are thought to have been formed by the collapse of ancient lava tubes – tunnels formed when lava flows beneath the solid crust. Leonardo Carrell Researchers from the University of Trento in Italy have discovered that the deepest part of these formations, the “The Pit of the Sea of TranquilityThese images were taken by NASA's Lunar Rover in 2010.
By comparing their simulations with lava tubes on Earth, the researchers found that the Mare Tranquillitatis hole appears to open into a large cavern buried at least 400 feet (130 meters) underground. The cave appears to be about 150 feet (45 meters) wide and at least 100 feet (30 meters) long, but could be much larger.
Caves like these could offer a unique window into the evolution of the Moon, says Carell. “Analyzing rocks from lunar caves, which have not been altered by the harsh lunar environment, could provide important insights into key scientific questions, such as the timeline and duration of volcanic activity on the Moon and the actual composition of the Moon's mantle,” Carell says.
The same stone ceiling that protects the cave rocks from the intense radiation experienced on the surface could also provide valuable shielding for future human explorers on the Moon. “Unlike the surface of the Moon, where temperatures change dramatically between day and night, [the caves] “It has a stable internal temperature, and it's also a natural shield against radiation and impacts,” Carrell says.
The idea of using natural caves like these as lunar base camps has long been popular, and future astronauts may one day call the Sea of Tranquility home.
topic:
- Moon/
- Space Exploration
Source: www.newscientist.com