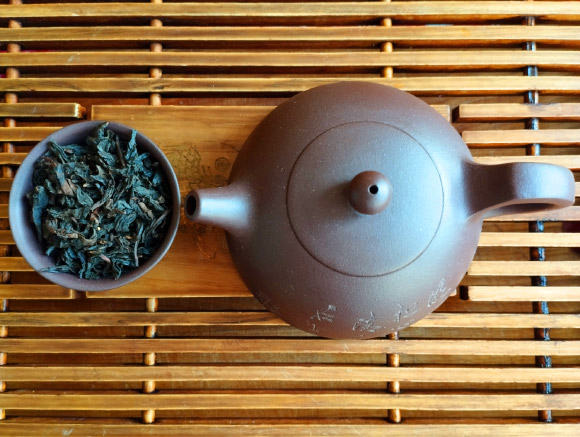
Free amino acids (FAA) specifically determine the quality of tea. Theaninewhich gives the tea its infusion flavor. However, its concentration varies widely depending on the type of tea, influencing both the flavor and nutritional profile of the tea. In a new study led by the Tea Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Huazhong Agricultural University, 339 tea lines were collected to study FAA levels to elucidate tea variation and accumulation mechanisms. The results provide insights and benefits for the conservation, evaluation, and utilization of tea germplasm, with the ultimate goal of tea plant genetic improvement and breeding, as well as further deciphering the complex complex traits of tea plants. We provide valuable information and approaches to help you.
By analyzing the variation of FAA of 339 tea accessions over 2 years, the determined components of FAA, including arginine, glutamine, glutamic acid, alanine, and theanine, with the highest diversity index were found in different genetic resources and within species. We found that there were differences between strains. On the other hand, the amount is Camellia sinensis All were significantly higher than their wild relatives. In this study, a significant opposite trend between chlorophyll and FAA profiles was identified. Image credit: Sci.News.
“Tea tree (Camellia sinensis) and its wild relatives, evergreens and woody perennials, belong to this genus. camellia “It is a member of the Camellia family with a long history of cultivation,” said co-senior author Dr. Liang Chen of the Tea Research Institute and colleagues.
“Originally in southwestern China, it is widely consumed around the world and is becoming the most important non-alcoholic beverage.”
“For commercial and quality value, the secondary metabolites of the tea plant are important criteria associated with pleasant flavor, nutritional value, and numerous health benefits, including polyphenols, catechins, caffeine, theanine, and terpenes. .”
“Therefore, the evaluation and utilization of tea lines… findings appear in this diary horticultural research.
_____
ron fan others. 2024. Comprehensive analysis of free amino acid variation and accumulation in tea lines. horticultural research 11 (1):uhad263;doi: 10.1093/hr/uhad263
Source: www.sci.news