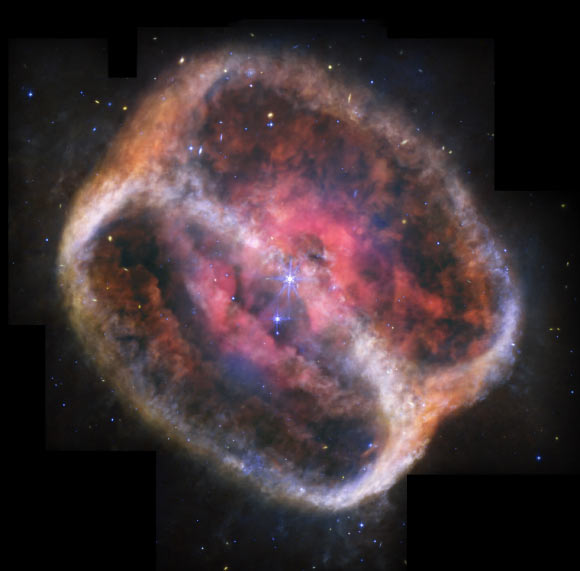
The two central stars of the NGC 1514 are displayed as one of the images from the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, forming this scene for thousands of years and maintaining it for thousands more.
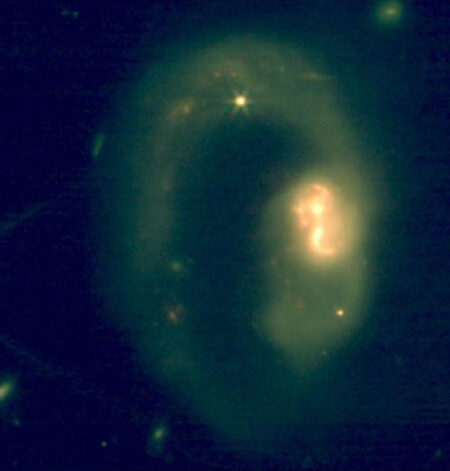
This web image shows the planetary nebula NGC 1514. Image credits: NASA/ESA/CSA/STSCI/Michael Ressler, JPL/Dave Jones, IAC.
NGC 1514 It is about 1,500 light years away from the Taurus sign.
The object, also known as the Crystal Ball Nebula, was discovered on November 13th, 1790 by German and British astronomer William Herschel.
He pointed out that NGC 1514 was the first deep sky object that really looked cloudy. He couldn’t resolve what he saw on individual stars in the cluster, like other objects he catalogued.
The ring around NGC 1514 was discovered in 2010, but Webb is now allowing astronomers to comprehensively examine the nature of the turbulent flow of this nebula.
“This scene has been formed for at least four,000 years and will continue to change over a thousand years,” Webb Astronomers said in a statement.
“In the center there are two stars that appear as one in Webb observations, caused by vivid diffraction spikes.”
“The star follows a solid, elongated nine-year orbit, covered in an arc of dust, represented by orange.”
“One of these stars, once a massive scale several times larger than our sun, played the lead role in producing this scene.”
“When the outer layers of the star were exhausted, only the hot, compact core was left behind.”
“As a white dwarf star, its winds rose sharply and weakened, and could have blown away the material into a thin shell.”
New Webb observations show that the nebula is at a 60-degree angle, which makes it appear that the can is poured in, but it is much more likely that the NGC 1514 took the shape of an hourglass and dropped the edges.
“Look for pinchwaist hints near the top left and bottom right. The dust is orange and drifts in a shallow V-shaped shape,” the astronomer said.
“When the star reached its peak of losing material, our peers may have become very close and have had these unusual shapes.”
“Instead of creating a sphere, this interaction may have instead formed a ring.”
“The NGC 1514’s outline is most clear, but the hourglass also has some sides of the 3D shape.”
“Look for a dim, translucent orange cloud between the rings that give to the nebula body.”
Nebula’s two rings are illuminated unevenly by Webb’s observations, appearing to be more diffused at the bottom left and top right.
Researchers believe that the rings are primarily made up of very small dust grains. This will get hot enough for Webb to detect when hit by ultraviolet rays from a white star star.
“In addition to dust, Webb revealed oxygen in its chunky pink center, especially at the edges of the bubbles and holes,” they said.
Source: www.sci.news