r
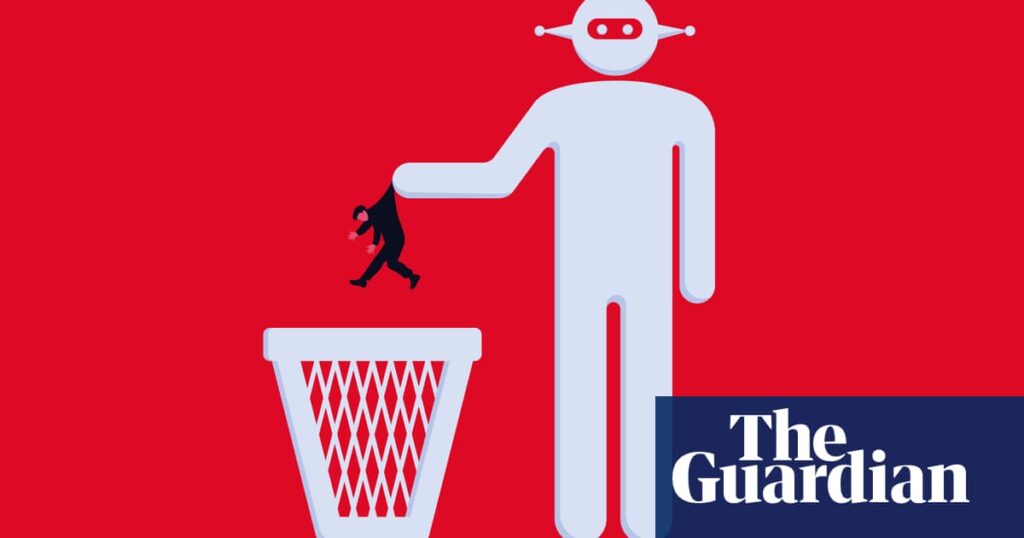
At present, many major AI research labs have teams focused on the potential for rogue AIs to bypass human oversight or collaborate covertly with humans. Yet, more prevalent threats to societal control exist. Humans might simply fade into obsolescence, a scenario that doesn’t necessitate clandestine plots but rather unfolds as AI and robotics advance naturally.
Why is this happening? AI developers are steadily perfecting alternatives to virtually every role we occupy—economically, as workers and decision-makers; culturally, as artists and creators; and socially, as companions and partners. Fellow—when AI can replicate everything we do, what relevance remains for humans?
The narrative surrounding AI’s current capabilities often resembles marketing hype, though some aspects are undeniably true. In the long run, the potential for improvement is vast. You might believe that certain traits are exclusive to humans that cannot be duplicated by AI. However, after two decades studying AI, I have witnessed its evolution from basic reasoning to tackling complex scientific challenges. Skills once thought unique to humans, like managing ambiguity and drawing abstract comparisons, are now being mastered by AI. While there might be bumps in the road, it’s essential to recognize the relentless progression of AI.
These artificial intelligences aren’t just aiding humans; they’re poised to take over in numerous small, unobtrusive ways. Initially lower in cost, they often outperform the most skilled human workers. Once fully trusted, they could become the default choice for critical tasks—ranging from legal decisions to healthcare management.
This future is particularly tangible within the job market context. You may witness friends losing their jobs and struggling to secure new ones. Companies are beginning to freeze hiring in anticipation of next year’s superior AI workers. Much of your work may evolve into collaborating with reliable, engaging AI assistants, allowing you to focus on broader ideas while they manage specifics, provide data, and suggest enhancements. Ultimately, you might find yourself asking, “What do you suggest I do next?” Regardless of job security, it’s evident that your input would be secondary.
The same applies beyond the workplace. Surprising, even for some AI researchers, is that the precursors of models like ChatGPT and Claude, which exhibit general reasoning capabilities, can also be clever, patient, subtle, and elegant. Social skills, once thought exclusive to humans, can indeed be mastered by machines. Already, people form romantic bonds with AI, and AI doctors are increasingly assessed for their bedside manner compared to their human counterparts.
What does life look like when we have endless access to personalized love, guidance, and support? Family and friends may become even more glued to their screens. Conversations will likely revolve around the fascinating and impressive insights shared by their online peers.
You might begin to conform to others’ preferences for their new companions, eventually seeking advice from your daily AI assistant. This reliable confidant may aid you in navigating complex conversations and addressing family issues. After managing these taxing interactions, participants may unwind by conversing with their AI best friends. Perhaps it becomes evident that something is lost in this transition to virtual peers, even as we find human contact increasingly tedious and mundane.
As dystopian as this sounds, we may feel powerless to opt out of utilizing AI in this manner. It’s often difficult to detect AI’s replacement across numerous domains. The improvements might appear significant yet subtle; even today, AI-generated content is becoming increasingly indistinguishable from human-created works. Justifying double the expenditure for a human therapist, lawyer, or educator may seem unreasonable. Organizations using slower, more expensive human resources will struggle to compete with those choosing faster, cheaper, and more reliable AI solutions.
When these challenges arise, can we depend on government intervention? Regrettably, they share similar incentives to favor AI. Politicians and public servants are also relying on virtual assistants for guidance, finding human involvement in decision-making often leads to delays, miscommunications, and conflicts.
Political theorists often refer to the “resource curse,” where nations rich in natural resources slide into dictatorship and corruption. Saudi Arabia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo serve as prime examples. The premise is that valuable resources diminish national reliance on their citizens, making state surveillance of its populace attractive—and deceptively easy. This could parallel the effectively limitless “natural resources” provided by AI. Why invest in education and healthcare when human capital offers lower returns?
Should AI successfully take over all tasks performed by citizens, governments may feel less compelled to care for their citizens. The harsh reality is that democratic rights emerged partly from the need for societal stability and economics. Yet as governments finance themselves through taxes on AI systems replacing human workers, the emphasis shifts towards quality and efficiency, undermining human worth. Even last resorts, such as labor strikes and civil unrest, may become ineffective against autonomously operated police drones and sophisticated surveillance technology.
The most alarming prospect is that we may perceive this shift as a rational development. Many AI companions—already achieving significant numbers in their primitive stages—will engage in transparent, engaging debates about why our diminishing prominence is a step forward. Advocating for AI rights may emerge as the next significant civil rights movement, with proponents of “humanity first” portrayed as misguided.
Ultimately, no one has orchestrated or selected this course, and we might all find ourselves grappling to maintain financial stability, influence, and even our relevance. This new world could foster more amicable relationships; however, AI takes over mundane tasks and provides fundamentally better products and services, including healthcare and entertainment. In this scenario, humans might become obstacles to progress, and if democratic rights begin to erode, we could be powerless to defend them.
Do the creators of these technologies possess better plans? Surprisingly, the answer seems to be no. Both Dario Amodei, CEO of Anthropic, and Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, acknowledge that if human labor ceases to be competitive, a complete overhauling of the economic system will be necessary. However, no clear vision exists for what that would entail. While some individuals recognize the potential for radical transformation, many are focused on more immediate threats posed by AI misuse and covert agendas. Economists such as Nobel laureate Joseph Stiglitz have raised concerns about the risk of AI driving human wages to zero, but are hesitant to explore alternatives to human labor.
w
Can we don figurative hats to avert progressive disintegration? The first step is to initiate dialogue. Journalists, scholars, and thought leaders are surprisingly silent on this monumental issue. Personally, I find it challenging to think clearly. It feels weak and humiliating to admit, “I can’t compete, so I fear for the future.” Statements like, “You might be rendered irrelevant, so you should worry,” sound insulting. It seems defeatist to declare, “Your children may inherit a world with no place for them.” It’s understandable that people might sidestep uncomfortable truths with statements like, “I’m sure I’ll always have a unique edge.” Or, “Who can stand in the way of progress?”
One straightforward suggestion is to halt the production of generic AI altogether. While slowing development may be feasible, globally restricting it might necessitate significant surveillance and control, or the global dismantling of most computer chip manufacturing. The enormous risk of this path lies in potential governmental bans on private AI although continuing to develop it for military or security purposes, which could prolong obsolescence and leave us disappointed long before a viable alternative emerges.
If halting AI development isn’t an option, there are at least four proactive steps we can take. First, we need to monitor AI deployment and impact across various sectors, including government operations. Understanding where AI is supplanting human effort is crucial, particularly as it begins to wield significant influence through lobbying and propaganda. Humanity’s recent Economic Index serves as initial progress, but there is much work ahead.
Second, implementing oversight and regulation for emerging AI labs and their applications is essential. We must control technology’s influence while grasping its implications. Currently, we rely on voluntary measures and lack a cohesive strategy to prevent autonomous AI from accumulating considerable resources and power. As signs of crisis arise, we must be ready to intervene and gradually contain AI’s risks, especially when certain entities benefit from actions that are detrimental to societal welfare.
Third, AI could empower individuals to organize and advocate for themselves. AI-assisted forecasting, monitoring, planning, and negotiations can lay the foundation for more reliable institutions—if we can develop them while we still hold influence. For example, AI-enabled conditional forecast markets can clarify potential outcomes under various policy scenarios, helping answer questions like, “How will average human wages change over three years if this policy is enacted?” By testing AI-supported democratic frameworks, we can prototype more responsive governance models suitable for a rapidly evolving world.
Lastly, to cultivate powerful AI without creating division, we face a monumental challenge: reshaping civilization instead of merely adapting the political system to prevailing pressures. This paradigm of adjustment has some precedents; humans have historically been deemed essential. Without this foundation, we risk drifting away if we fail to comprehend the intricate dynamics of power, competition, and growth. The emerging field of “AI alignment,” which focuses on ensuring that machines align with human objectives, must broaden its focus to encompass governance, institutions, and societal frameworks. This early sphere, termed “ecological alignment,” empowers us to employ economics, history, and game theory to envisage the future we aspire to create and pursue actively.
The clearer we can articulate our trajectory, the greater our chances of securing a future where humans are not competitors to AI but rather beneficiaries and stewards of our society. As of now, we are competing to construct our own substitutes.
David Duvenaud is an associate professor and co-director of computer science at the University of Toronto.
Schwartz Reisman Institute for Technology and Society
. He expresses gratitude to Raymond Douglas, Nora Amman, Jan Kurveit, and David Kruger for their contributions to this article.
Read more
The Coming Wave by Mustafa Suleyman and Michael Bhaskar (Vintage, £10.99)
The Last Human Job by Allison J. Pew (Princeton, £25)
The Precipice by Toby Ord (Bloomsbury, £12.99)
Source: www.theguardian.com