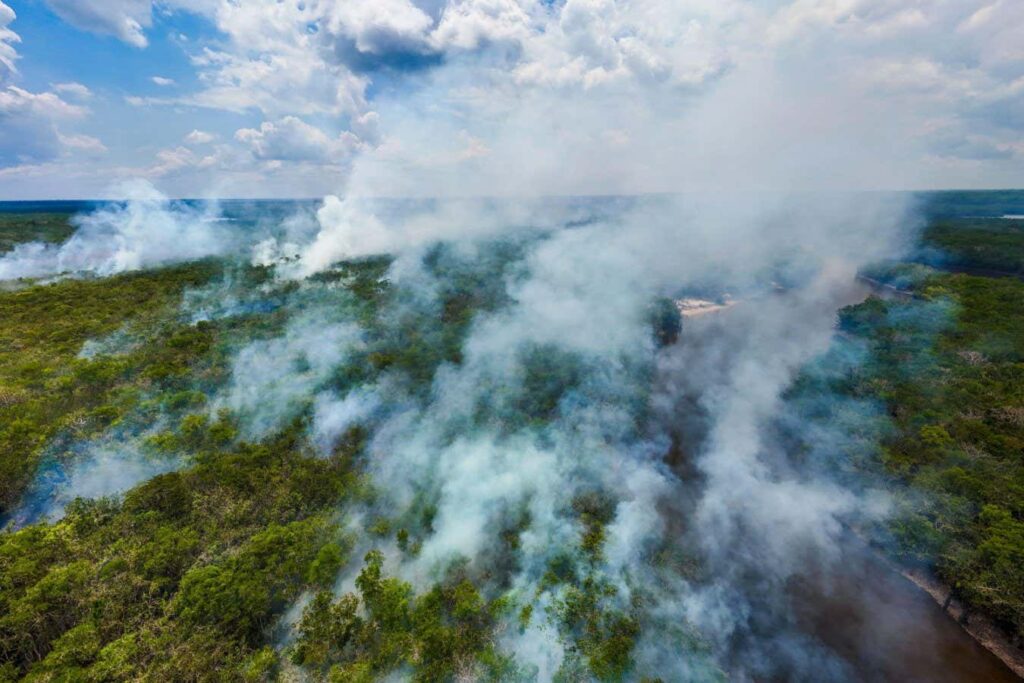
Wildfires raging in the Amazon rainforest
Fernando Lessa/Alamy
Numerous forest-related carbon offset initiatives certified by Verra, the largest carbon registry globally, face potential risks from wildfires and other disturbances that may hinder effective carbon release from the atmosphere.
These forest-based carbon offset initiatives aim to conserve or restore forests to produce carbon credits, which can be sold to corporations or individuals to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Such schemes are designed to maintain a “buffer pool” of unsold carbon credits as insurance against future carbon losses due to factors like wildfires, pests, or severe weather events. Nevertheless, assessments of these buffer pools indicate that current carbon offset strategies are likely not sufficiently secured.
“The figures don’t really rely on scientific evidence, as far as we know,” stated William Anderegg from the University of Utah. A spokesperson from Verra defended the organization’s methodology, asserting that the determination of buffer pool size is grounded in rigorous, science-based risk evaluations, stressing that replenishment should align with what buffer-immersed projects have collected.
Buffer pools pose a significant challenge, especially when forest-based carbon credits are sold to offset emissions from fossil fuels that may have been in the atmosphere for centuries. “If you’re attempting to sequester carbon into trees, you need to guarantee its stability over an extended period,” Anderegg remarked.
In principle, by safeguarding adequate carbon to counterbalance potential losses over decades, a large buffer pool would suffice. However, previous research by Anderegg and his team revealed that forest carbon projects certified by Verra typically secured only 2% of their credits for protection against natural risks.
To evaluate whether this is an adequate safeguard, Anderegg and his colleagues employed ecological models to calculate the necessary size of the buffer to effectively manage the risk posed by natural disturbances across various tropical forest types. They juxtaposed these findings with the buffer pools currently mandated for Verra certification.
The results indicated that Verra’s standards fall short of ensuring permanent carbon storage in nearly all scenarios. In certain instances, the required buffer could be 11 times smaller than necessary. “Given these natural hazards, [the buffer] should be at least doubled, if not more, to be fitting,” Anderegg noted.
A Verra representative mentioned that the majority of the 76 million carbon credits presently within the buffer pool are utilized. They added, “previous reversals suggest that the buffer is not overwhelmed.” “The ongoing maintenance of buffer pools over time clearly demonstrates their effectiveness despite the risk of reversals,” the spokesperson stated.
Buffer pools are not merely a concern for Verra. For instance, California’s regulated carbon offset program has faced wildfires in recent years. A significant portion of the buffer pool was designed to endure for a century.
This concern is anticipated to grow as forest carbon losses escalate. “To secure sustainability extending beyond 100 years, you must ensure that the buffer is sufficiently robust to confront multiple climate variations,” Anderegg concluded.
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com