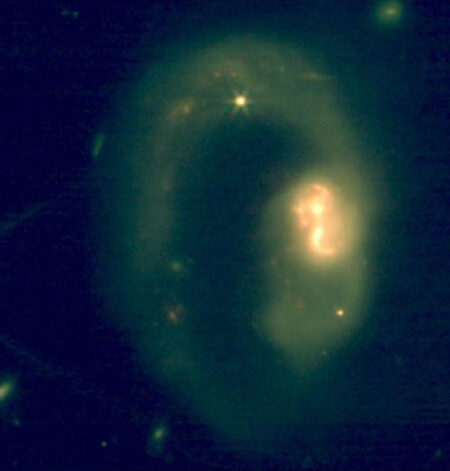
Among the four fundamental forces in the universe, gravity often comes to mind when considering cosmic phenomena. This is quite logical, as gravity operates over vast distances, exerting its influence on massive objects, making it the most significant and far-reaching force. However, another essential force, known as electromagnetism, also plays a critical role in the study of space.
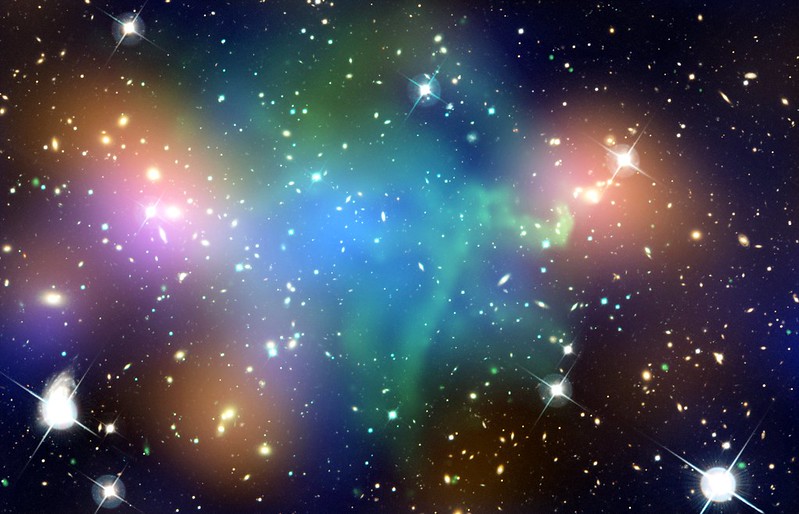
To begin with, all light is made up of electromagnetic radiation, which consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. This includes everything from radio waves to visible light and X-rays. Similar to Earth and the Sun, many celestial bodies are enveloped in magnetic fields. The Earth’s magnetic field serves as a shield against harmful radiation, while the solar magnetic field repels it. The generation of a magnetic field requires the movement of charged particles, such as protons and electrons. Consequently, a variety of objects, including entire galaxies, possess magnetic fields!
Researchers are aware that galaxies have magnetic fields, but it remains uncertain how various galaxies develop different magnetic intensities or how these fields influence their evolution over time. This investigation is further complicated by the fact that galaxies often exist in clusters. For instance, the Milky Way is surrounded by smaller galaxies known as satellites, which exert gravitational pull on each other and interfere with each other’s magnetic fields.
The research team explored how diverse environments in smaller galaxies affected the strength of their magnetic fields. They approached this by simulating the motion of materials within the galaxy as if they were liquids filled with striped particles. Two sets of simulations were conducted, the second of which also included the effects of high-energy particles known as cosmic rays.
In total, they simulated magnetic fields across 13 distinct scenarios, ranging from isolated galaxies with masses 10 billion times that of the Sun to those 10 trillion times greater, accompanied by up to 33 satellites. Each simulation commenced with galaxies exhibiting a magnetic field strength of 10-14 Gauss (g). For context, Earth’s magnetic field strength is about 0.3-0.6 g. The scenarios were evolved over 12 billion simulation years, allowing galaxies to interact, traverse space, and form stars, subsequently tracking the magnetic field strength in smaller galaxies.
Throughout the simulated timeline, the magnetic fields of all galaxies strengthened as star formation progressed. The birth of stars stirs the galactic matter, enhancing magnetic field strength and producing cosmic rays. Most galaxies concluded with magnetic fields ranging from 10-7 to 10-6 G, with larger galaxies typically achieving stronger fields. Interestingly, the researchers found that small galaxies passing in close proximity to larger companions exhibited stronger magnetic fields than equivalent isolated galaxies.
They monitored satellite galaxies over a series of simulations and discovered that, on average, magnetic field strength increased by 2-8 times as these galaxies approached their host. In extreme cases, the satellite’s magnetic field intensified by up to 15 times after nearing the host. In contrast, satellite galaxies that were more distant or had not yet approached their host did not show such significant increases in magnetic field strength.
The researchers interpret their findings to suggest that the more turbulent the interstellar medium (ISM) within a galaxy, the greater the strength of its magnetic field. Orbiting near a host galaxy tends to disturb the ISM of the satellite galaxy, rendering it more magnetic than a solitary small galaxy. Approaching a massive galaxy compresses the satellite, exposing it to magnetizing materials, and both interactions contribute to amplifying the magnetic field strength.
The team recommends that future studies utilize these results to inform radio and gamma-ray observations of galaxies, as these two segments of the electromagnetic spectrum can provide astronomers insights into the magnetic field properties of celestial bodies. They also caution that astronomers conducting simulations of isolated galaxies might yield skewed results since such a scenario does not accurately reflect the reality in which many galaxies are in proximity to companions.
Post view: 177
Source: sciworthy.com