by
A groundbreaking study investigated the complex relationship between Earth’s surface temperature and emitted longwave radiation, revealing deviations from the expected quaternary pattern. This research improves our understanding of climate sensitivity and the factors that influence it, such as greenhouse gases and atmospheric dynamics. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Climate science research has revealed new insights into the relationship between surface temperature and emitted longwave radiation, challenging traditional models and improving our understanding of Earth’s climate sensitivity.
Want to know what causes Earth’s climate sensitivity? Recent research shows Advances in atmospheric science. We investigate a complex relationship that transforms the relationship between surface temperature and outgoing longwave radiation (OLR) from fourth-order to sublinear. Led by Dr. Jie Sun florida state university this study elucidates the hidden mechanisms that shape Earth’s climate and provides new insights into why the relationship between temperature and OLR deviates from the fourth-order pattern described by the Stefan-Boltzmann law. Masu.
Stefan-Boltzmann law and climate dynamics
What is the Stefan-Boltzmann law? Atmospheric greenhouse gases create a contrast between surface heat release and OLR, which is related to the fourth power of surface temperature.
Professor Hu Xiaoming of Sun Yat-sen University, corresponding author of the study, explained: This allows the relationship between surface temperature and OLR to follow a quartic pattern, since the radiation-emitting layer is lowered. ”
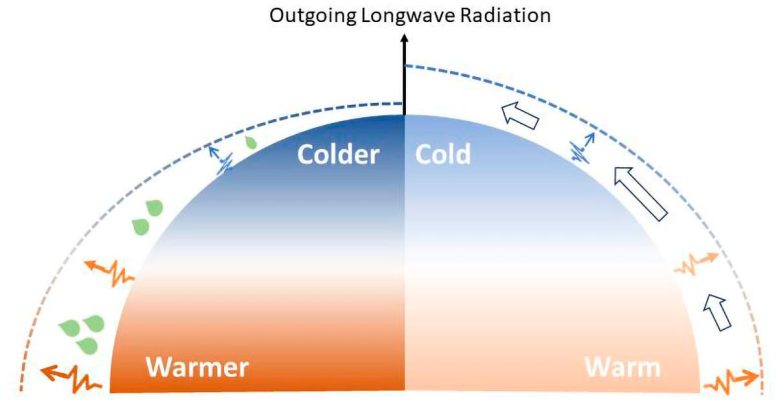
Diagram showing two main processes: sublinear surface temperature and outgoing longwave radiation (OLR). Left: Increased meridional surface temperature gradient due to the greenhouse effect of water vapor. Right: Poleward energy transport reroutes part of the OLR from warmer to colder regions. Credit: Ming Cai and Xiaoming Hu
Factors affecting surface temperature and OLR
This study reveals how various factors influence surface temperature and OLR. The water vapor greenhouse effect acts as a magnifying glass, amplifying temperature differences across the Earth’s surface without changing the latitudinal variation of the OLR. This suppresses the nonlinearity between OLR and surface temperature.
Polar energy transport, on the other hand, acts as an equalizer to harmonize temperature differences across different regions of the Earth. One of the by-products of this global heat redistribution is the rerouting of OLR from warmer to colder regions, which acts to reduce the differences in OLR between different regions. This further suppresses nonlinearities.
“Understanding these complex climate interactions is like deciphering a puzzle. Each piece brings us closer to deciphering the complexity of Earth’s climate,” said Ming Kai, a professor at Florida State University. Masu.”
By uncovering these relationships, scientists are learning more about Earth’s climate and how its complex components regulate overall climate sensitivity, i.e., not just the rate of energy output, but also where the output occurs to make significant progress in understanding.
Reference: “Sublinear relationship between planetary outward longwave radiation and surface temperature in a gray atmosphere radiative-convective transport climate model” Jie Sun, Michael Secor, Ming Cai, Xiaoming Hu, November 25, 2023. Advances in atmospheric science.
DOI: 10.1007/s00376-023-2386-1
Source: scitechdaily.com