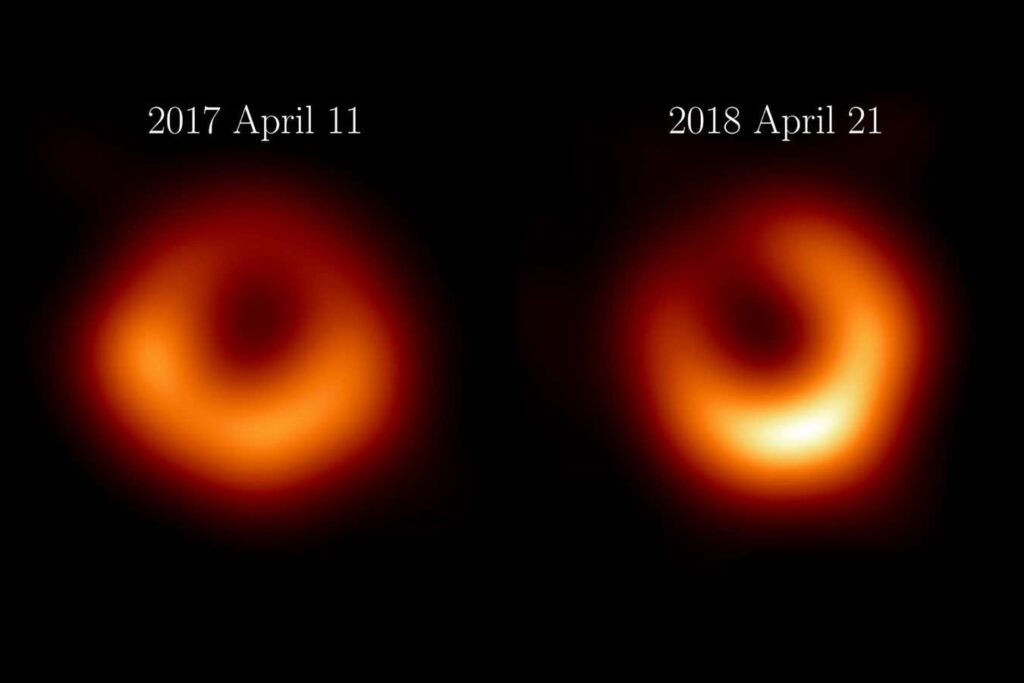
The image on the right is the latest and best image of a black hole.
EHT collaboration
Thanks to an update to the world’s first black hole image taken a year later, we now have the most detailed observation of a black hole to date.
In 2019, researchers released an image of the supermassive black hole known as M87*, located 55 million light-years away at the center of galaxy M87. The image, the world’s first glimpse of a black hole, was taken during the first observations in 2017 by a network of radio astronomical observatories around the world called the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT).
Now, the EHT collaboration has released tracking images of M87* taken during 2018 observations using additional telescopes in Greenland.
As the name suggests, these objects do not emit light, so the light in the image does not come out of the black hole. What we see instead is the silhouette of a black hole at the center of a mass of hot material, pulled inward by its powerful gravity.
“This image tells us that the black hole’s shadow is permanent and still exists,” says the EHT scientist. Eduardo Ross. “You can see that the ring is a beautiful circle. It’s very circular, not an oval or anything. We also see an enhancement on the south side in this ring, which is what we expected.”
This enhancement, visible as a slightly bright glow under the slightly displaced shadow of M87*, is due to the distortion of space-time associated with the black hole’s rotation (as explained by Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity). This is due to
The additional telescopes have slightly increased the resolution of the images, greatly increasing the amount of data that can be cross-referenced with observations from other telescopes. However, less than ideal weather made viewing conditions difficult. This means the resolution is not as high as theoretically expected, Ross says.
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com