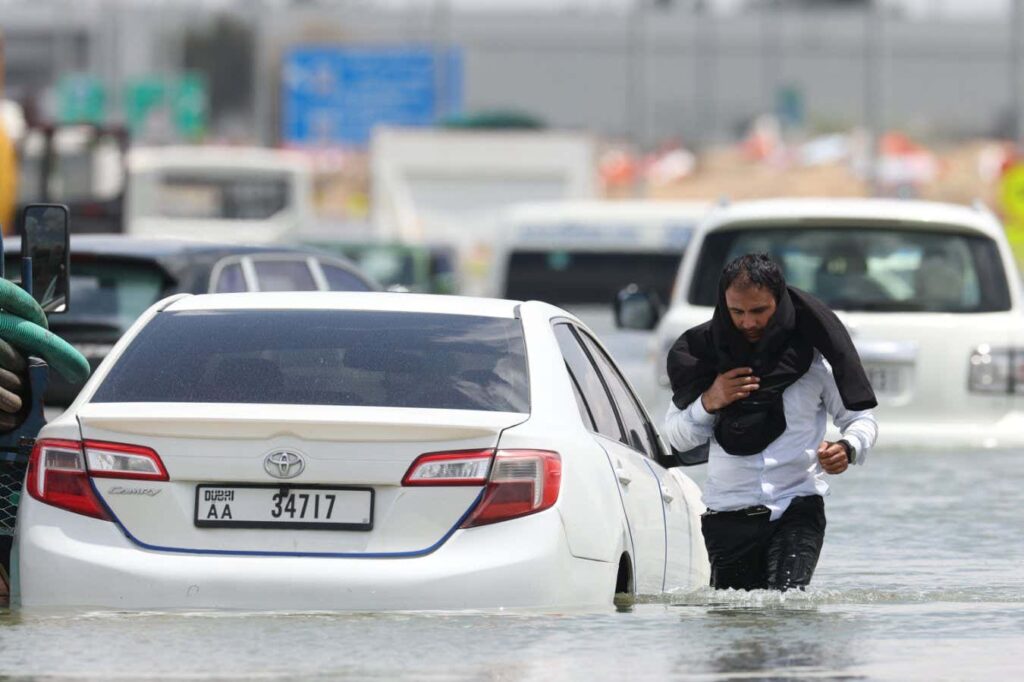
Driver abandons car after rainstorm in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, April 17
Christopher Pike/Bloomberg/Getty
Record rainfall has hit the Arabian Peninsula this week, causing flooding in Dubai, Abu Dhabi and other coastal cities in the United Arab Emirates. The extreme weather sparked speculation on social media that the UAE’s long-standing cloud seeding program may have played a role. However, cloud seeding almost certainly does not have a significant impact on flooding.
How unusual was the recent rain in the Arabian Peninsula?
It was the most extreme event in the UAE since record-keeping began in 1949. according to to the state-run Emirates News Agency. From April 15th to 16th, some parts of the country received more than their normal annual rainfall in a 24-hour period. Heavy rains in desert regions are not uncommon, but they are not unheard of – as the UAE sees it. heavy rain and flooding For example, 2016.
A drainage system in a coastal city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been overwhelmed by spills, causing flooding. Dramatic images of a plane driving through stagnant water at Dubai International Airport have been widely shared online.
In neighboring Oman, died in flash flood At least 18 people. Parts of Bahrain, Qatar and Saudi Arabia also experienced unusual rainfall.
What is cloud seeding? Did it affect extreme rain?
Cloud seeding is a way to increase precipitation, From about the 1940s. This involves spraying powders such as silver iodide onto clouds from airplanes or rockets, or burning them from stations on the ground. Droplets of supercooled water form around these particles and fall to the ground as rain or snow.
Since 2002, the UAE has maintained one of the largest cloud seeding programs in the world. Planes regularly fly cloud-seeding missions in an effort to increase freshwater resources in arid regions.
Meteorologists at the UAE’s National Center of Meteorology (NCM) have further fueled speculation that cloud formations may be responsible for the recent rains. Said bloomberg news That in the days before the storm, planes had spread clouds over the country. However, NCM later stated: statement That no seed was sown during the storm.
“We take the safety of our employees, pilots and aircraft very seriously,” the company said. “NCM does not conduct cloud seeding operations during extreme weather conditions.”
Even if cloud formation had occurred during the storm, it would have had at most a small effect on precipitation and would have been localized. The extent of rainfall across several countries and the generally limited influence of cloud species suggest that cloud occurrence almost certainly does not play a significant role. “There is no technology that can create or even significantly alter this type of rainfall event.” Maarten Ambaum at the University of Reading, UK statement.
He noted that cloud seeding would have little impact on clouds that were already predicted to bring rain to the region. And that assumes that cloud seeding is effective at all.
“Many claims of successful cloud seeding are false, scientifically flawed, or actually fraudulent,” he says. Andrew Dessler at Texas A&M University. “This makes most atmospheric scientists very skeptical about cloud formation.”
What weather factors were behind the rain?
The extreme precipitation was caused by large storms called mesoscale convective systems. Suzanne Gray Researchers at the University of Reading say this happens “when many individual thunderstorms coalesce to form a single large high-level cloud shield.”
Forecasters had predicted a high risk of flooding in the area for at least a week before the storm.Writing in progress XJeff Berardelli, a meteorologist at WFLA-TV in Florida, linked the storm to a blocking pattern created by a slow-moving jet stream.
Has climate change made rain worse?
Further analysis is needed to link this particular event to climate change, but climate change likely plays a role.
“These types of heavy rainfall events are likely to become more extreme with climate change, as a warming atmosphere retains more water vapor,” Ambaum said. Changes in temperature can also affect atmospheric circulation patterns in the form of changes in precipitation.
For example, recent study The same type of storm that caused this extreme rainfall has occurred in the region 95 times since 2000, with the most frequent occurrences on the Arabian Peninsula in March and April, researchers found. However, it has also been found that the duration of these storms has increased over the UAE since 2000, which may be linked to rising temperatures.
Alternative climate modeling study They predict that annual rainfall in the UAE will increase by 10 to 25 percent by mid-century, characterized by more intense precipitation events.
topic:
- climate change/
- Abnormal weather
Source: www.newscientist.com