Electrically conductive cable bacteria are a group of multicellular prokaryotes enabling electron transfer across centimeter-scale distances in both marine and freshwater sediments. Biologists have successfully isolated and characterized new species of cable bacteria from the Mudflat at the intertidal estuary mouth in Yaquina Bay, Oregon, USA.
Microscopic investigation of cable bacteria Ca. Electrothrix yaqonensis, yb6 strain. Image credit: Hiral et al., doi: 10.1128/aem.02502-24.
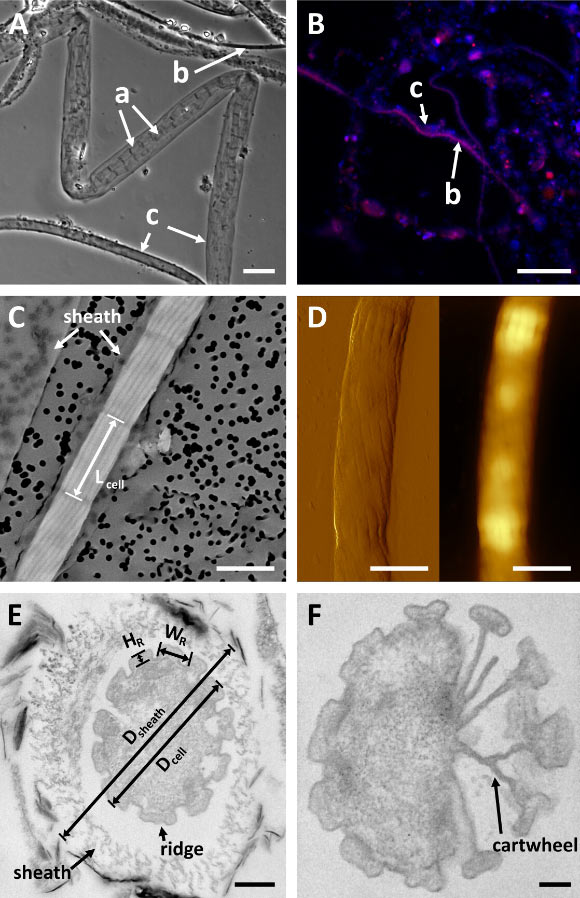
“Cable bacteria are filamentous prokaryotes that engage in electrosulfide oxidation in the upper layers of aquatic sediments,” states Dr. Chen Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at Oregon State University, along with her team.
“Their electrogenetic metabolism features a unique division among cells in multicellular filaments, facilitating the migration of electrons from deeper sediment layers to the surface, where sulfide oxidation occurs.
“This long-range electron transport is enabled by a specialized network of conductive fibers, which run in parallel ridges from one end of the filament to the other.”
“These fibers connect through conductive contoured structures at the cell interfaces, ensuring redundancy within the electrical network.”
The new species is referred to as Ca. Electrothrix yaqonensis, isolated from the mudflat of Yaquina Bay, Oregon.
“This new species represents a bridge and appears to be an early branch of the Ca. Electrothrix clades, suggesting it offers new insights into the evolution and functionality of these bacteria across various environments,” remarks Dr. Li.
“It differentiates itself from other known cable bacterial species through its significant metabolic potential and distinctive structural traits, including surface ridges that are three times more pronounced than those in other species.
“These bacteria have the capacity to transport electrons for environmental cleanup, potentially aiding in the removal of harmful substances from sediments.”
“Moreover, the highly conductive nickel proteins they produce can lead to advancements in bioelectronics.”
Ca. Electrothrix yaqonensis derives its name from the Jacona people, whose ancestral lands span the Bay of Yaquina.
“Following the tribe’s recognition of its historical connection to the land, it has honored these ecologically significant bacteria and acknowledged their ongoing contributions to sustainability and ecological wisdom,” said Dr. Li.
The team’s study was published this week in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology.
____
Anwar Hyalal et al. A new cable bacterial species with distinct morphology and genomic potential. Appl Environ Microbiol Published online on April 22, 2025. doi:10.1128/aem.02502-24
Source: www.sci.news