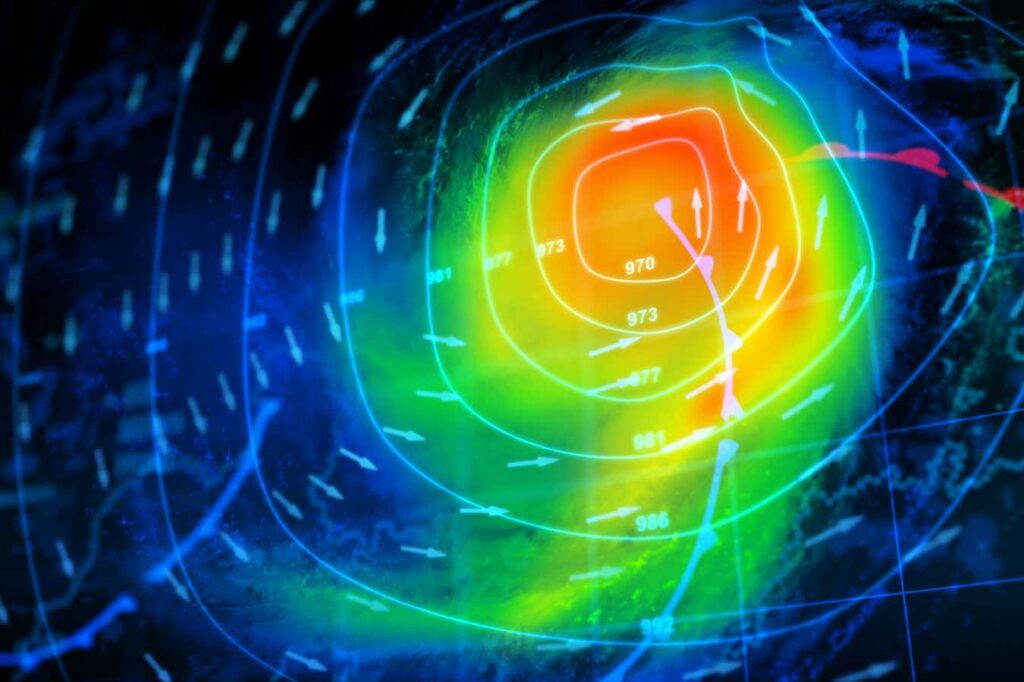
Weather forecasting today relies on simulations that require large amounts of computing power.
Petrovich9/Getty Images/iStockphoto
Google DeepMind claims its latest weather forecasting AI can predict faster and more accurately than existing physics-based simulations.
GenCast is the latest in DeepMind's ongoing research project to improve weather forecasts using artificial intelligence. The model was trained on 40 years of historical data from the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). ERA5 ArchiveThis includes regular measurements of temperature, wind speed, and barometric pressure at various altitudes around the world.
Data up to 2018 was used to train the model, and then 2019 data was used to test predictions against known weather conditions. The company found that it outperformed ECMWF's industry standard ENS forecasts 97.4% of the time, and 99.8% of the time when forecasting more than 36 hours ahead.
Last year, DeepMind collaborated with ECMWF to create an AI that outperformed the “gold standard” high-resolution HRES 10-day forecast by more than 90%. Previously, he developed a “nowcasting” model that used five minutes of radar data to predict the probability of rain over a given one square kilometer area from five to 90 minutes in advance. Google is also working on ways to use AI to replace small parts of deterministic models to speed up calculations while maintaining accuracy.
Existing weather forecasts are based on physical simulations run on powerful supercomputers to deterministically model and estimate weather patterns as accurately as possible. Forecasters typically run dozens of simulations with slightly different inputs in groups called ensembles to better capture the variety of possible outcomes. These increasingly complex and large numbers of simulations are computationally intensive and require ever more powerful and energy-consuming machines to operate.
AI has the potential to provide lower-cost solutions. For example, GenCast uses an ensemble of 50 possible futures to create predictions. Using custom-built, AI-focused Google Cloud TPU v5 chips, each prediction takes just 8 minutes.
GenCast operates at a cell resolution of approximately 28 square kilometers near the equator. Since the data used in this study were collected, ECMWF's ENS has been upgraded to a resolution of just 9 kilometers.
Yilan price DeepMind says AI doesn't have to follow, and could provide a way forward without collecting more detailed data or performing more intensive calculations. “If you have a traditional physics-based model, that's a necessary requirement to solve the physical equations more accurately, and therefore to get more accurate predictions,” Price says. “[With] machine learning, [it] It is not always necessary to go to higher resolution to get more accurate simulations and predictions from your model. ”
david schultz Researchers at the University of Manchester in the UK say AI models offer an opportunity to make weather forecasts more efficient, but they are often over-hyped and rely heavily on training data from traditional physically-based models. states that it is important to remember that
“is that so [GenCast] Will it revolutionize numerical weather forecasting? No, because in order to train a model, you first have to run a numerical weather prediction model,” says Schulz. “These AI tools wouldn't exist if ECMWF didn't exist in the first place and without creating the ERA5 reanalysis and all the investment that went into it. It's like, 'I can beat Garry Kasparov at chess. But only after studying every move he's ever played.''
Sergey Frolov Researchers at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) believe that further advances in AI will require higher-resolution training data. “What we're basically seeing is that all of these approaches are being thwarted.” [from advancing] “It depends on the fidelity of the training data,” he says. “And the training data comes from operational centers like ECMWF and NOAA. To move this field forward, we need to generate more training data using higher-fidelity physically-based models. .”
But for now, GenCast offers a faster way to perform predictions at lower computational costs. kieran hunt A professor at the University of Reading in the UK believes ensembles can improve the accuracy of AI predictions, just as a collection of physics-based predictions can produce better results than a single prediction. states.
Mr Hunt points to the UK's record temperature of 40C (104C) in 2022 as an example. A week or two ago, there was only one member of the ensemble who was predicting it, and they were considered an anomaly. Then, as the heat wave approached, the predictions became more accurate, providing early warning that something unusual was about to happen.
“You can get away with it a little bit if you have one member who shows something really extreme. That might happen, but it probably won't happen,” Hunt says. “I don’t think it’s necessarily a step change; it’s a combination of new AI approaches with tools we’ve been using in weather forecasting for a while to ensure the quality of AI weather forecasts. There is no doubt that this will yield better results than the first wave of AI weather forecasting.”
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com