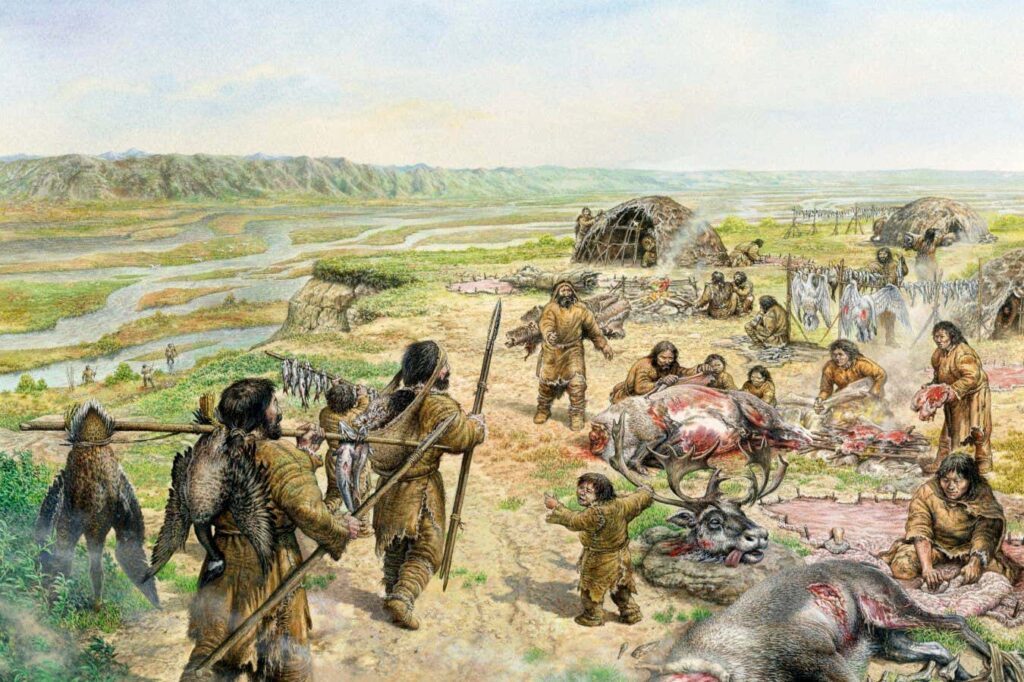
Early hunter-gatherers faced with food shortages may have benefited from the impulsivity associated with ADHD
John Civic/Science Photo Library
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may have evolved in hunter-gatherer societies because it was an advantage for them, according to the results of a new study. Characteristics commonly associated with the disease, such as impulsivity, cause some foragers to move from areas where resources are depleted to areas with richer harvests faster than areas without the disease. It could have been something like this.
ADHD affects people's behavior, which can result in them acting impulsively and having trouble concentrating. Although its exact cause is not fully understood, the condition tends to run in families.
Its origins are similarly unknown, he says. Arjun Ramakrishnan At the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. “Is it a remnant of the hunter-gatherer world?”
To explore this, Ramakrishnan, david barak Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania recruited 506 people in the United States to play an online foraging game. Players were instructed to collect as many berries as possible in 8 minutes by moving their cursor over the bush.
They were given the choice of staying in the bush or trying their luck in another bush that might have more or less fruit. Moving to a new bush also resulted in a short timeout, so players had to balance the chance of getting more berries with the time lost by moving.
Before playing the game, participants completed a questionnaire assessing whether they had symptoms of ADHD, such as difficulty concentrating or restlessness.
People with ADHD symptoms spent about four seconds hovering over a particular bush compared to those without symptoms, and as a result, the former group collected an average of 521 berries. However, I was able to collect 602 berries.
The findings suggest that selective pressures faced by early hunter-gatherer societies, such as lack of food and other resources, may have driven the evolution of ADHD. There may have been some foraging situations in which it was better to stay than move on, but Barak said this tendency to leave could have been an advantage in some scenarios.
“Humans and other apes are very sophisticated foragers, but like almost all other animals, we tend to stay in our plots too long and harvest too much in our fields.” he says. “Therefore, starting action early may be beneficial to reduce over-harvesting, and this may be where the impulsive characteristics of ADHD come in handy.”
Although many people around the world are no longer looking for food, situations still exist where similar decision-making processes occur. If a person is studying for an exam, he may start by looking at one resource. If it doesn't help you understand the topic, Barak says, you may quickly switch to another resource, which may be more efficient and helpful.
“Although it is difficult to determine exactly how ADHD-related behaviors were adaptive in past environments, we find that people with and without ADHD show measurable differences in foraging strategies. In that sense, these results are convincing,” says Dr. Dan Eisenberg at the University of Washington in Seattle.
but Annie Swanepoel North East London NHS Foundation Trust said it did not reflect the scarcity of resources experienced by many of the early hunter-gatherers, as foraging operations produced abundant berry crops.
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com