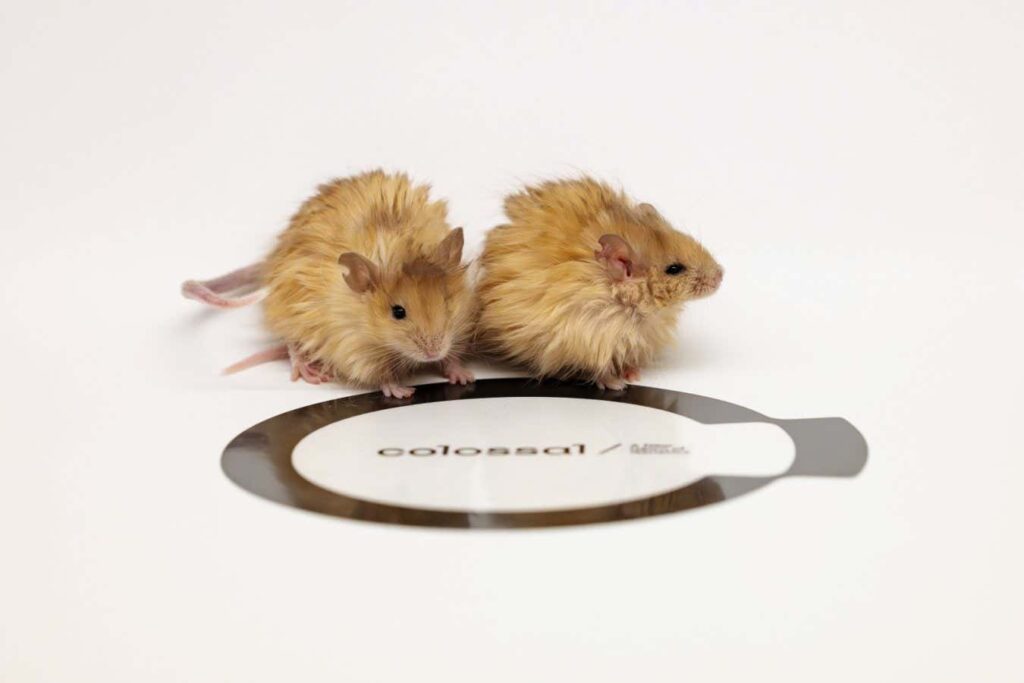
Mouse modified to give a “mammoth-like” coat
Huge
There is Estimated genetic differences of 1.5 million Between wool mammoth and an Asian elephant. Colossal Biosciences, a company that seeks to revive extinct species through genetic engineering, now makes mice with “mammoth-like” fur, each with up to five genetic changes. It seems there's still a way to go.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xq9mvp_gg9y
Certainly, these mice have long, curly hair and blonde hair. In that way, it resembles a wool mammoth coat stored in permafrost. However, it is not clear that bringing the same genetic alterations in Asian elephants with far fewer hairs per area of the skin will result in similar results.
“The work done with these mice doesn't mean there's a solution ready to regain the huge phenotype,” says team members. I love Darren At Stockholm University in Sweden, on the Scientific Advisory Committee of Corosal. “As you point out, we also need to understand how to grow more fur.”
Creating an Asian elephant with these genetic changes would also be much more difficult than doing it in a mouse. “Engineering mutations in mice are an established process and are not particularly challenging.” Dusko Ilic King's College London.

Mouse that has been fixed and unfixed
Huge
Techniques that work in mice often fail in other species, and the size of elephants and their slow breeding significantly increases the time and cost involved. “These methods have not been developed for elephants. They are not easy based on anatomy.” Vincent Lynch At Buffalo University, New York. “That's probably the biggest challenge.”
However, Lynch is undoubtedly achievable. surely, Thomas Hildebrandt At the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research in Berlin, Germany – Another giant advisor – New Scientist His team is the first time they've collected eggs from elephants, but the results have not yet been made public. Egg collection is an important step in IVF and is a genetic modification of mammals.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QGT8SOKDSXO
So how did Colossal make a “mammoth” mouse? Researchers began by looking for known mutations in mice that looked like fur. “[T]The majority of these genes were selected based on previous observations of the coat phenotype in mice,” read in a paper published today, which has not been peer-reviewed.
They identified eight genes that affect patterns (curse), color and hair length when disabled in mice. According to Colossal, one of these eight is a mammoth and is naturally disabled.
From the mammoth genome, the team identified small mutations that are thought to affect hair patterns, along with another disordered gene involved in fat metabolism.
The company then tried to modify these genes in mice. For example, one experiment used CRISPR gene editing to attempt to disable five of these genes in fertilized eggs. From 134 edited eggs, 11 puppies were born, and one of these puppies invalidated copies of both five genes.

Fur stored in frozen mammoth rank
Arami Stock Photo
In another study, the researchers used a form of CRISPR called base editing to abolish several genes in embryonic mouse stem cells. They combined this with another technique called homologous recombination to create the exact mutations found in the mammoth genome. Make accurate changes is much more difficult than disabling genes, but the recombination method works well only in the mouse.
The team then sequenced the cells to identify cells with the desired change and injected into mouse embryos to create chimeric mice. Of the 90 injected embryos, seven mice were born with four intended changes.
These experiments can be said to be successful in producing several mice with desirable physical changes in the fur, but only one genetic change is in exact agreement with what is found in the mammoth genome. It takes more work to achieve Colossal's stated purpose With the creation of “a cold-resistant elephant with all the core biological properties of wool mammoths,” and the elephant pregnancy lasting for about two years, Colossal is in time for a spontaneous 2028 deadline.
“Elephants with fur are not mammoths in the way we think of them.” Juan Antonio Rodriguez At the University of Copenhagen, Denmark. He says many of the 1.5 million differences between the mammoth and the Asian elephant genome may not be effective, but it is not clear which is more important.
Even if we did, it's dangerous to make broader changes, says Rodriguez. “The more things change in organisms, the more likely they are to tinker with major metabolic pathways and genes.”
Rodriguez, Lynch and Irik are all
Source: www.newscientist.com