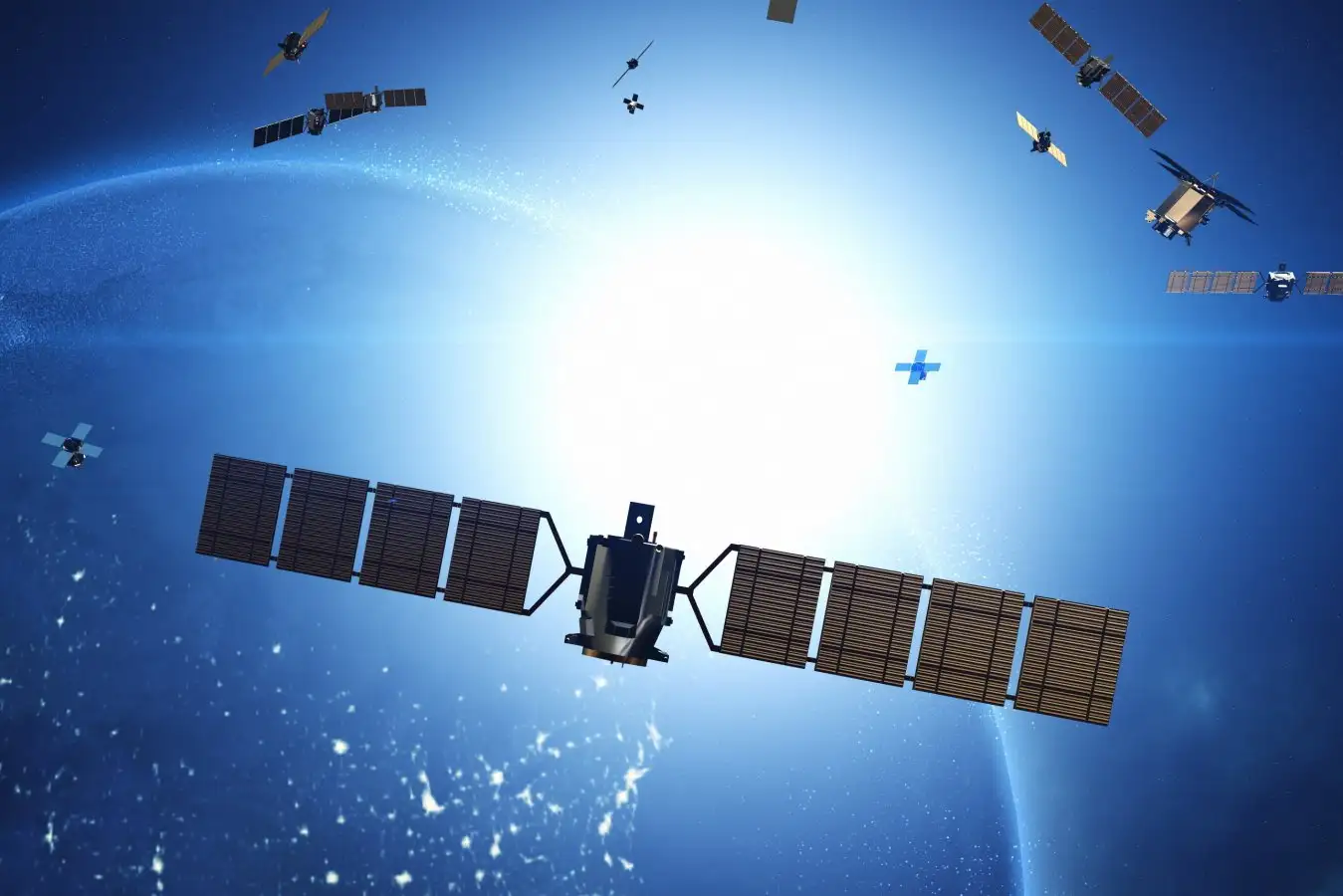
An artistic representation of a satellite in Earth’s orbit Yusery Yilmaz/Shutterstock
In the event that all satellites ceased their ability to maneuver, a collision would likely happen in just 2.8 days, underscoring the dense nature of Earth’s orbital space.
Over the past seven years, the number of satellites has more than tripled, soaring from 4,000 to nearly 14,000. A significant factor driving this surge is SpaceX’s Starlink program, which currently includes over 9,000 satellites situated in low Earth orbit between 340 and 550 kilometers above our planet.
This dramatic rise necessitates that satellites frequently adjust their positions to avoid collisions, which could create thousands of metal fragments and make parts of Earth’s orbit unusable. This process is referred to as a collision avoidance maneuver.
Between Dec. 1, 2024, and May 31, 2025, SpaceX executed 144,404 collision avoidance maneuvers within the constellation, averaging one every 1.8 minutes, per company reports. Notably, there has only been one documented orbital collision. In 2009, a functioning satellite from Iridium Communications collided with a defunct Russian Cosmos satellite, leaving hundreds of debris scattered in orbit.
Sarah Thiele and researchers from Princeton University utilized publicly available satellite tracking data to simulate the impact of increasing satellite numbers on collision risk. They introduced a novel measure named the Collision Realization And Significant Harm (CRASH) Clock to evaluate this risk. The title draws parallels to the well-known Doomsday Clock, which symbolizes the imminent threat of nuclear warfare. “We discussed it extensively,” he notes. Samantha Lawler, another team member from the University of Regina in Canada, contributed to this effort.
Their findings revealed that if all satellites in orbit as of 2018 (prior to the inaugural Starlink launch in 2019) suddenly lost control, a collision would have been imminent within 121 days. Presently, due to the surge in operational satellites, this timeframe has drastically reduced to a mere 2.8 days.
“We were astonished by how short it was,” Thiele comments.
The 2.8 days assumes a scenario where an event—such as a severe solar storm—renders all satellites incapable of altering their trajectories. In May 2024, a significant solar storm caused some Starlink satellites to react dramatically. A recurrence of the Carrington Event, the strongest solar storm on record from 1859, might bring serious challenges; Wind Vatapally from Luxembourg’s SES Satellites believes not all satellites would be incapacitated at once. “It would be implausible for all of them to fail simultaneously,” he states.

Astronomy Capital: Chile
Explore Chile’s astronomical treasures. Discover the most advanced observatory and gaze at the stars in some of the clearest skies on the planet.
Indicators like the crash clocks serve to emphasize the congested state of Earth’s orbit, he remarks. Hugh Lewis from the University of Birmingham in the UK questions, “Can we keep piling on this precarious structure?” He adds, “The more elements you introduce, the greater the risk of a collapse when problems arise.”
With plans for tens of thousands more satellites to be launched in the coming years by SpaceX, Amazon, and various Chinese enterprises for their extensive constellations, it’s plausible that the CRASH clock will indicate an even shorter timeframe, raising the potential for collisions. “It’s quite frightening to consider,” Thiele adds.
Topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com