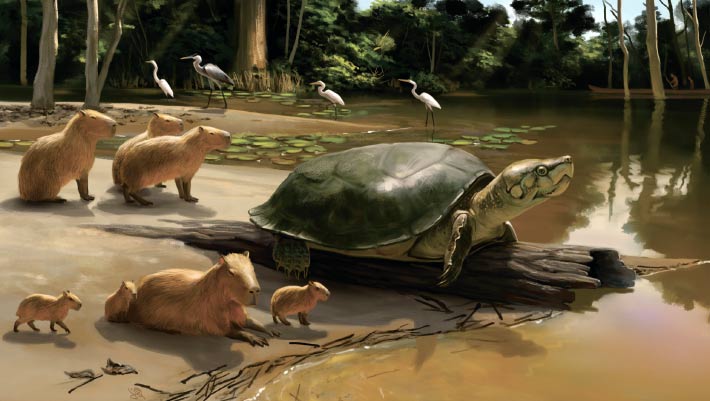
Pertocephalus maturin Its shell length probably reaches about 1.8 meters (5.9 ft), making it one of the largest freshwater turtles ever discovered. The discovery marks the latest known occurrence of giant freshwater turtles and suggests coexistence with early humans in the Amazon.
The newly discovered turtle species lived in what is now Brazil during the late Pleistocene, between 40,000 and 9,000 years ago.
named Pertocephalus maturinthe ancient animal may have reached a carapace length of about 1.8 meters.
Dr. Gabriel Ferreira, a paleontologist at the Senckenberg Center, said: “Freshwater turtles, in contrast to their terrestrial and marine relatives, rarely have such gigantic morphologies and are the only known species to date. “This is very surprising since the youngest giant fossils come from Miocene deposits.” Human Evolution and Paleoenvironment at the University of Tübingen.
“The carapace is up to 1.4 meters (4.6 feet) long; Asian narrow soft-shelled turtle (chitra chitra) The length is approximately 1.1 m (3.6 ft). South American river turtle (Podocnemis Expansa) They are some of the largest freshwater turtles alive today. ”
“In the past, only a few freshwater turtles with carapace lengths exceeding 1.5 meters (4.9 feet) were known,” he added.
“Such megafauna are most recently known, mainly from the Miocene period, about 23 million to 5 million years ago.”
huge partial lower jaw Pertocephalus maturin It comes from the Rio Madeira layer.
This specimen was collected by gold miners at a site known as the Taclas Quarry in Porto Velho in the Brazilian Amazon.
Morphological and phylogenetic analyzes of this fossil revealed close kinship with modern Amazonian species and suggested an omnivorous diet.
“Pertocephalus maturin “This is the youngest known giant freshwater turtle and suggests coexistence between this ancient species and early human residents of the Amazon region,” the paleontologists said.
“People settled in the Amazon region about 12,600 years ago. We also know that large turtles have been a food source for humans since the Paleolithic period.”
“Freshwater turtles are much more difficult to catch because of their agility, but we wonder if early humans also ate them.” Pertocephalus maturin It is not yet clear whether they fell victim to human expansion along with South American megafauna. ”
“Here we need further data from late Pleistocene and early Holocene deposits in the Amazon basin,” Dr. Ferreira said.
discovery of Pertocephalus maturin is reported in paper in a diary biology letters.
_____
GS Ferreira other. 2024.Latest freshwater giants: new Peltocephalus (Pleurodira: Podocnemididae) A late Pleistocene turtle of the Brazilian Amazon. Biol.Let 20(3):20240010; doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2024.0010
Source: www.sci.news