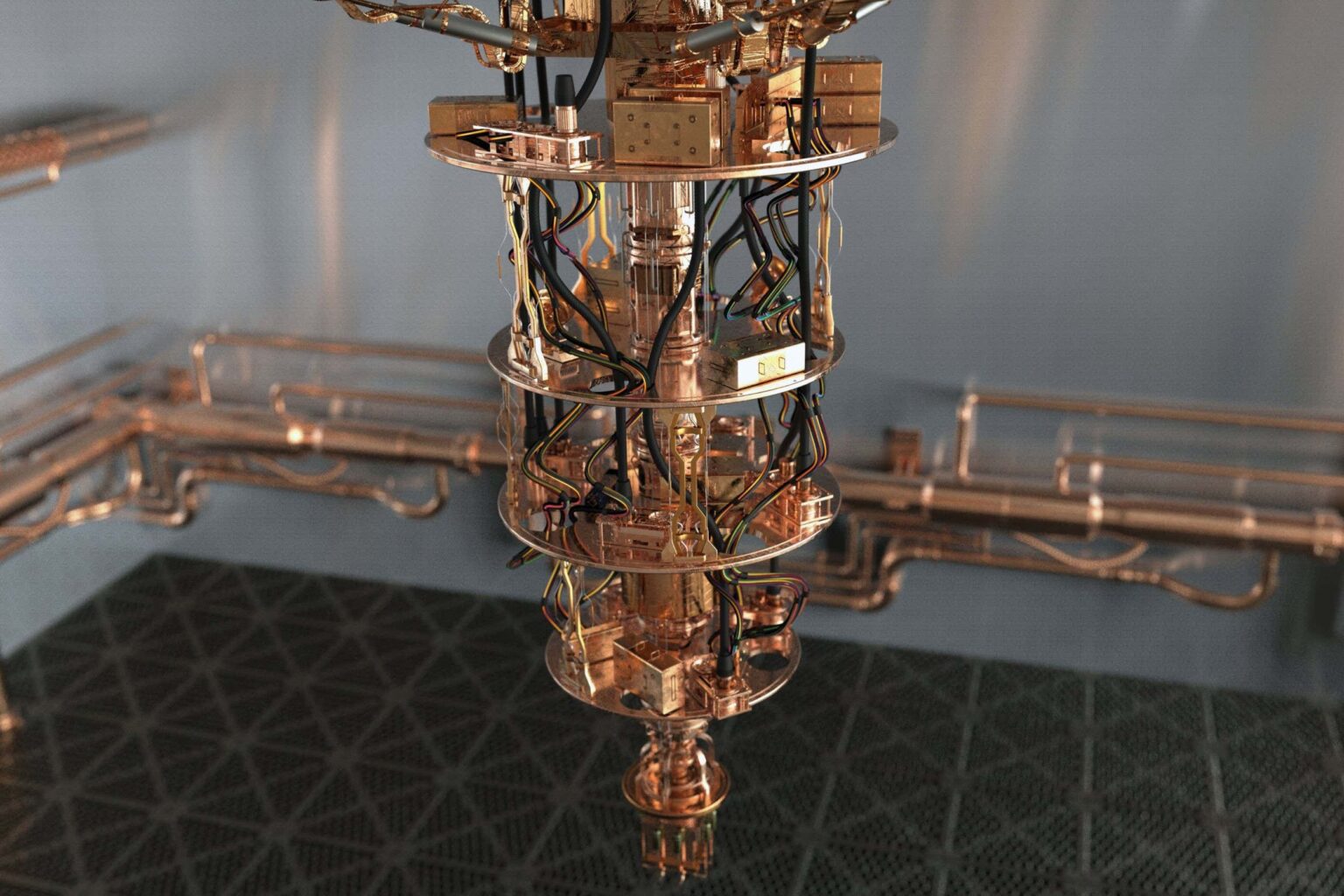
Exports of quantum computers are restricted in many countries
Saigh Anys/Shutterstock
As a result of secret international negotiations, governments around the world have imposed identical export controls on quantum computers while refusing to disclose the scientific rationale behind the controls. Although quantum computers could theoretically threaten national security by breaking encryption technology, even the most advanced quantum computers currently publicly available are too small and error-prone to achieve this, making the bans seem pointless.
The UK: Quantum computers with more than 34 quantum bits (qubits) and error rates below a certain threshold. The intention seems to be to limit machines with certain capabilities, but the UK government has not stated this explicitly. New Scientist A Freedom of Information request seeking the basis for these figures was denied on national security grounds.
France has also imposed similar export controls. Quantum Bits The numbers and error rates are also improving, as are Spain and the Netherlands. Having the same limits across European countries might suggest EU regulation, but this is not the case. A spokesperson for the European Commission said: New Scientist EU member states are free to adopt national, rather than bloc-wide, measures when it comes to export controls. “The recent quantum computer restrictions by Spain and France are an example of such national measures,” they said. They declined to explain why the figures for the EU's various export bans are completely consistent if these decisions were taken independently.
A spokesman for the French Embassy in London said: New Scientist The limits were set at a level “likely to indicate a cyber risk,” they said. They noted that the regulations are the same in France, the UK, the Netherlands and Spain because of “multilateral negotiations that took place over several years under the Wassenaar Arrangement.”
“The limits chosen are based on scientific analysis of the performance of quantum computers,” the spokesperson said. New ScientistBut when asked for clarification about who carried out the analysis and whether its findings would be made public, a spokesman declined to comment further.
of Wassenaar Agreement The system, which is followed by 42 participating countries including EU member states, the UK, the US, Canada, Russia, Australia, New Zealand and Switzerland, controls the export of items with potential military applications, known as dual-use technologies. The export ban on quantum computers also includes similar language regarding 34 qubits..
New Scientist We wrote to dozens of Wassenaar member states asking whether there was quantum-computer-level research that posed a risk to export, whether it had been made public, and who had conducted it. Only a few countries responded.
“We closely monitor other countries as they introduce national restrictions on certain technologies,” a spokesperson for the Swiss Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs, Education and Research said, “but in specific cases it is already possible to block the export of such technologies using existing mechanisms.”
“We are closely following the Wassenaar discussions on the exact technical control parameters for quantum.” Milan Godin, Belgian Advisor to the EU Working Party on Dual-Use Goods, Belgium. China does not appear to have implemented its own export controls yet, but Godin said quantum computers are a dual-use technology. It has the potential to crack commercial or government codes, and its speed could ultimately enable militaries to plan faster and better, including for nuclear missile attacks.
A spokesperson for Germany's Federal Office for Economics and Export Control confirmed that the export restrictions on quantum computers are the result of negotiations under the Wassenaar Agreement, but Germany does not appear to have implemented any restrictions. “The negotiations are confidential and unfortunately we cannot provide any details or information about the considerations of the restrictions,” the spokesperson said.
Christopher MonroeThe co-founder of quantum computing company IonQ said industry participants have been aware of similar bans and are discussing their criteria, but he doesn't know where they come from.
“I don't know who decided the logic behind these numbers,” he says, but it may have something to do with the threshold for simulating a quantum computer with a regular computer. This gets exponentially harder as the number of qubits increases, so Monroe thinks the rationale behind the ban may be to limit quantum computers that are too advanced to simulate, even though such devices have no practical use.
“It would be a mistake to think that just because we can't simulate the behavior of a quantum computer doesn't mean it's useful, and severely restricting research into advances in this grey area would certainly stifle innovation,” he says.
topic:
- safety/
- Quantum Computing
Source: www.newscientist.com