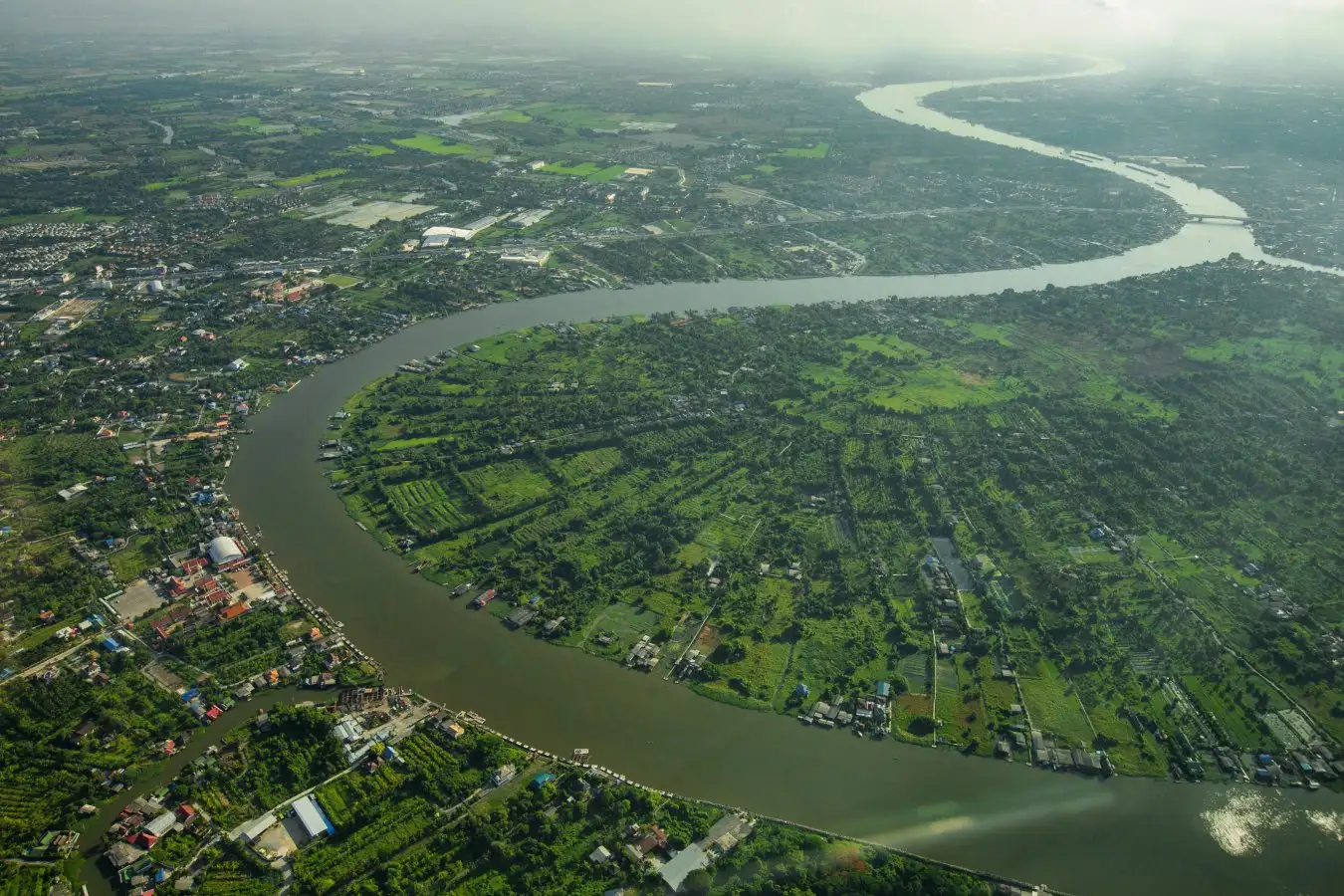
Thailand’s Chao Phraya River Delta: Rapidly Sinking Channon Kanjanavasoonthara/Getty Images
The Chao Phraya River Delta, one of the most economically and environmentally vital deltas globally, is sinking at alarming rates, threatening millions with severe flooding. Recent satellite data analysis reveals that subsidence in river deltas is becoming a greater danger to local communities than rising sea levels.
Approximately 500 million people inhabit this delta, including some of the world’s most impoverished communities. This expansive lowland area houses 10 megacities, each boasting populations exceeding 10 million.
Manuchel Shirzai and his team at Virginia Tech researched subsidence rates in 40 global deltas, including the Mekong, Mississippi, Amazon, Zambezi, Yangtze, and Nile rivers.
Shirzaei noted, “As deltas sink, global sea levels are also rising by about 4 millimeters annually, creating a compounded risk of flooding.”
The research utilized data from 2014 to 2023 collected by the European Space Agency’s Sentinel 1 satellite radar, which can detect changes in ground distance with precision up to 0.5 mm. Across the 40 studied deltas, over one-third showed signs of subsidence, with more than half of the area affected in 38 of these regions.
“In numerous cases, land subsidence contributes more to relative sea level rise than the ocean itself,” Shirzaei asserted. “In 18 out of 40 deltas, average subsidence rates surpass sea level rise, with the impacts being significantly pronounced in areas located less than 1 meter above sea level.”
The Chao Phraya Delta, where Bangkok is situated, ranks as the most affected among 40 nations concerning subsidence rates and impacted areas. Here, the average subsidence rate reaches 8 mm per year, which is double the global average for sea level rise, with 94% of the delta sinking at rates above 5 mm per year.
As a result of combined land subsidence and sea level rise, Bangkok and the Chao Phraya Delta confront a formidable projected sea level rise of 12.3 millimeters per year. Other cities like Alexandria in Egypt and Jakarta and Surabaya in Indonesia share similar predicaments of rapid land subsidence.
The researchers analyzed three major anthropogenic pressures: groundwater extraction, sediment alteration, and urban growth to assess their impacts on delta subsidence. Shirzaei explained that upstream dams, levees, and river engineering limit sediment input, which is crucial for delta maintenance, while urban development escalates pressure on delta surfaces and heightens water demand, furthering groundwater depletion.
Among these factors, groundwater extraction poses the most significant impact overall, although specific delta areas may be more influenced by sediment shifts and urbanization, the study found.
Shirzaei emphasized, “It would be misguided for policymakers to concentrate solely on sea level rise due to climate change and overlook local land subsidence. Unlike global sea level rise, human-driven land subsidence can often be tackled locally through groundwater regulation, managed aquifer recharge, and sediment management.”
He also pointed out that water-intensive facilities, such as data centers, may exacerbate this issue. “Our findings reveal that groundwater extraction is a major contributor to accelerated land subsidence in numerous delta regions, which can worsen when such facilities depend on local water sources,” he remarked.
In already vulnerable areas like the Mekong Delta, increasing water demand may hasten land subsidence, jeopardizing drainage, flood protection systems, and the durability of crucial infrastructure. “This doesn’t suggest data centers should be avoided altogether in the delta, but they must prioritize groundwater conservation, minimize overall water use, and take land subsidence into account,” said Shirzaei.
Topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com