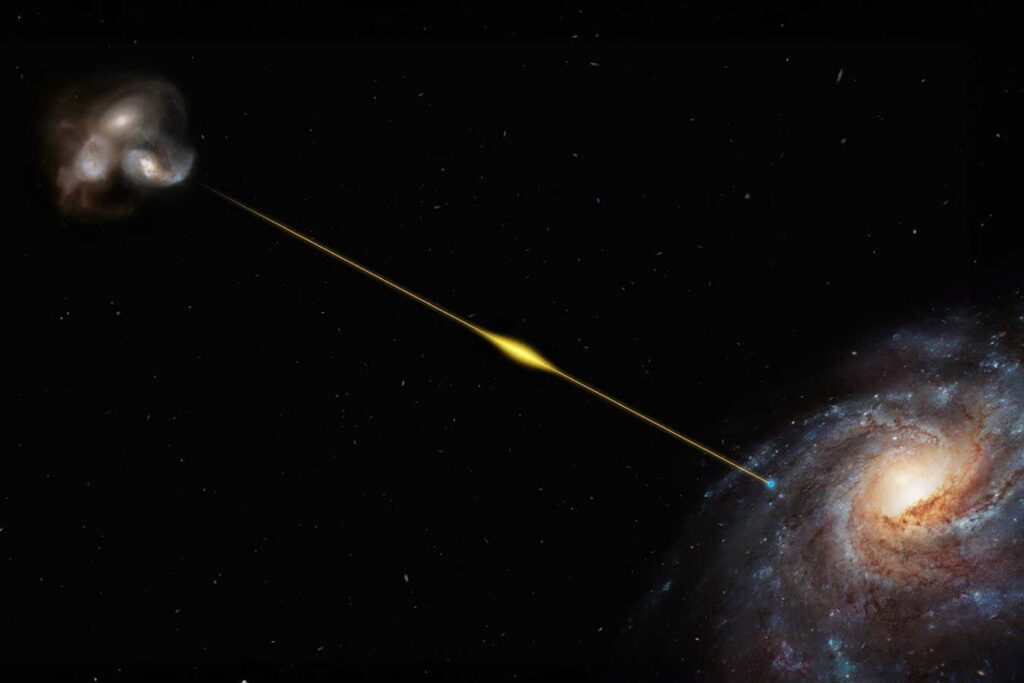
Artist's impression of the path of a fast radio burst (not to scale) FRB 20220610A
M. Kohnmesser/European Southern Observatory
The unexplained flash of radio waves that reached Earth in 2022 originated from a small group of galaxies about 8 billion light-years away. This discovery expands our understanding of how mysterious fast radio bursts (FRBs) form.
To date, astronomers have discovered more than 1,000 FRBs. FRBs are strange bursts of high-frequency electromagnetic radiation that cross the sky in just a few milliseconds. Some events repeat and are detected as blinking multiple times. The main explanation is that FRBs are produced by powerful spinning stars known as magnetars, highly magnetized spinning stars left behind after a massive star explodes as a supernova.
About 50 FRBs have been identified as the source of the Milky Way and other galaxies. But in 2022, astronomers discovered the most distant and powerful FRB yet: non-recurring FRB 20220610A, which dates back to when the universe was just 5 billion years old.
alexa gordon A team of researchers from Northwestern University in Illinois followed up on this finding. Researchers discovered in April 2023 using the Hubble Space Telescope that FRB 20220610A originates from a small dwarf galaxy. This galaxy was part of a compact group of seven galaxies so small that the entire galaxy fit within the Milky Way. “This is a very unusual system,” Gordon says. “At this distance of his FRB, only about 0.1 to 1 percent of galaxies belong to compact groups.”
Such groups are thought to be active regions of star formation. This supports FRB's explanation of magnetars, as they probably form early in a galaxy's evolution when hot, massive stars explode. In compact groups, “galaxies are interacting fairly frequently,” Gordon says. This triggers star formation consistent with what is seen in his FRB study, produced by newer, near-Earth sources.
This work was uploaded to the arXiv preprint server late last year and was also presented at today's presentation. Meeting of the American Astronomical Society in New Orleans.
This discovery further expands the types of environments in which FRBs are known to exist. “The majority are in star-forming spiral galaxies,” Gordon says. “But he also found FRBs in galaxy clusters, dwarf galaxies, and globular clusters. The addition of 'compact groups' to this list shows that we are finding his FRBs in a variety of locations.” Here's another example. ”
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com