The researchers: Pineapple Mint (Mint)This herb is highly valued for its unique aroma and medicinal properties.
Pineapple Mint (Mint) is cultivated worldwide for its unique aroma and commercial value. Image credit: Yang others., doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae022.
Genus MintThis plant, known as mint, is a type of herb with a strong scent. Lamiaceae.
This versatile plant contains a variety of components, including essential oils and non-essential compounds, making it suitable for a wide range of uses.
Mint Essential oils have a long history of medicinal use as digestive aids and pain relievers. Essential oils have a wide range of biological activities, including antioxidant, antibacterial, antiradiation, anticancer, and antihypertensive properties.
Pineapple mint is a cultivated variegated variety of apple mint.
It grows as a wild plant all over the world and is widely used in the medical field due to its many therapeutic properties.
“Despite their importance, understanding the genetic basis of these traits remains Mint “This gene is very unique, characterized by high heterozygosity and numerous structural mutations,” said Qi Song, PhD, of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and his colleagues.
“Comprehensive research Mint “Sequencing the genome was essential to uncover the genetic factors that influence its unique characteristics.”
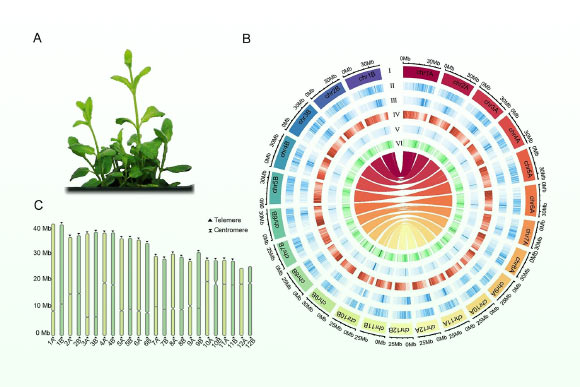
In this study, the researchers succeeded in generating the first high-quality, haplotyped genome assembly of pineapple mint, with a genome size of 414.3 Mb and 31,251 coding genes.
By integrating data from different sequencing platforms, we resolved two complete haplotype assemblies with nearly complete annotated telomeres and centromeres.
Remarkably, they uncovered 41,135 structural variations, including deletions, insertions, duplications, and translocations, many of which affect genes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis.
One important finding is that piperitenone oxide dominates among the volatile compounds produced by pineapple mint, in contrast to menthol, which is more common in other plants. Mint seed.
The authors identified three genes. Isopiperitenone reductase We identified ISPR, a key enzyme in menthol biosynthesis, but found that its low transcription level likely led to the accumulation of piperitenone oxide instead.
“The completion of the gap-free genome Mint “This is an important milestone in plant genomics,” Dr. Song said.
“This comprehensive genetic map provides a basis for investigating the molecular mechanisms underlying pineapple mint's unique properties, which may lead to innovative applications in medicine and agriculture.”
of result Published in the journal Horticultural Research.
_____
Hanting Yang others2024. Haplotyped gap-free genome assembly provides new insights into monoterpenoid diversification. Mint “Variegata”. Horticultural Research 11(3):uhae022; doi:10.1093/hr/uhae022
Source: www.sci.news