Black widow spider venom contains a cocktail of seven specific latrotoxins, but only one, alpha-latrotoxin, targets vertebrates, including humans. chemist of University of Munster They have now deciphered the structure of alpha-latrotoxin before and after membrane insertion at near atomic resolution.
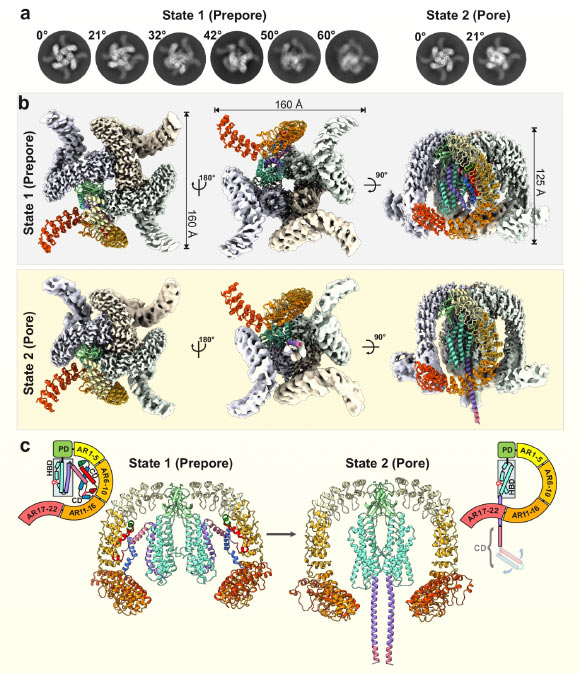
Cryo-EM structures of α-latrotoxin in two different tetrameric states. Image credit: Klink others., doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52635-5.
Latrotoxin is the main toxic component of the venom of black widow spiders (genus). latrodectus).
The toxins include five insecticidal toxins known as α-latrotoxin, α-, β-, γ-, δ-, and ε-latroinsect toxins, which are unique to vertebrates, and one toxin that is unique to crustaceans.
“Alpha-latrotoxin interferes with nervous system signal transmission,” said researcher Björn Klinck and colleagues at the University of Münster.
“As soon as alpha-latrotoxin binds to specific receptors at the synapse (contacts between nerve cells or between nerve cells and muscles), calcium ions flow uncontrollably into the presynaptic membrane of the signal-transmitting cell.”
“This triggers the release of neurotransmitters, which causes strong muscle contractions and spasms.”
“Although this process seems simple at first glance, there are very complex mechanisms behind it.”
To better understand the mechanism of calcium influx into the presynaptic membrane, the authors used high-performance cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and molecular dynamics (MD) computer simulations.
They showed that alpha-latrotoxin undergoes significant changes when it binds to the receptor.
Some of the toxic molecules form stalks and penetrate the cell membrane like a syringe.
As a special feature, this stalk forms small pores in the membrane, which act as calcium channels.
MD simulations revealed that calcium ions can enter the cells through a selection gate on the side directly above the pore.
“This toxin mimics the function of calcium channels in the presynaptic membrane in a very complex way,” said Christos Gatsogiannis, a researcher at the University of Münster.
“Therefore, it is different in every way from any toxin known to date.”
“The new discovery opens up a wide range of potential applications.”
“Latrotoxin has considerable biotechnological potential, including the development of improved antidotes, treatments for paralysis, and new biopesticides.”
of study Published in a magazine nature communications.
_____
Clink BU others. 2024. Structural basis of α-latrotoxin transition to cation-selective pores. Nat Commune 15, 8551; doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52635-5
Source: www.sci.news