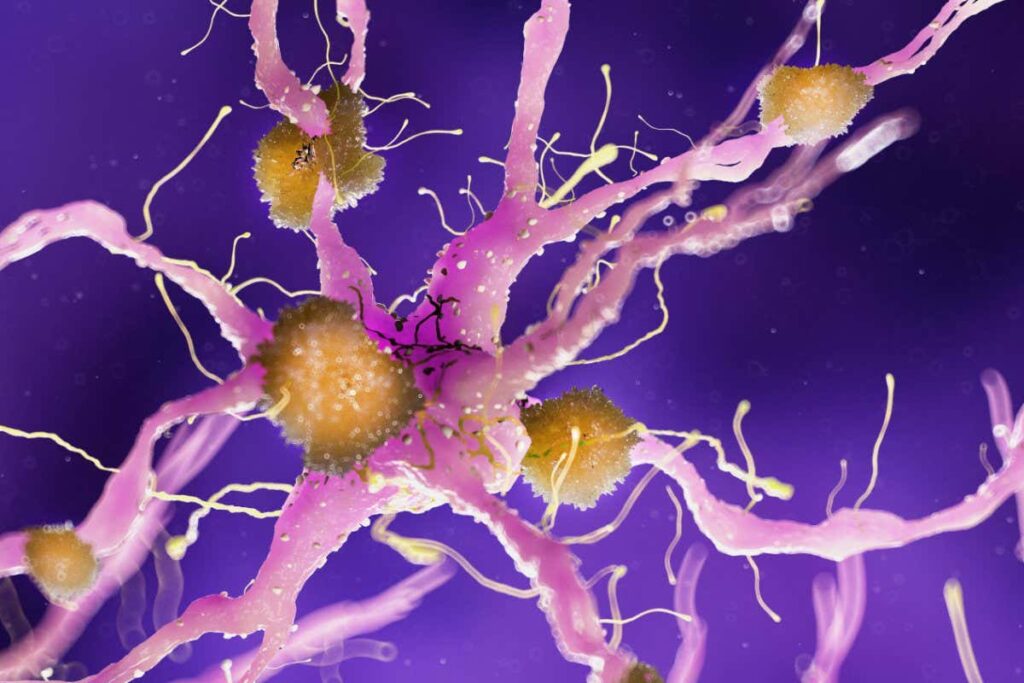
Protein plaques in the brain may be caused by mitochondrial dysfunction
Sebastian Kauritzky/Alamy
If you own a car, you’ve probably noticed that your engine becomes less efficient over time. The farther you drive, the more fuel it takes to cover the same distance. Eventually, you’ll end up with so little power that you need a physical push to climb a gentle hill.
It is now becoming clear that much the same holds true for the human brain. Microscopic structures called mitochondria, found in all brain cells, are literally the engines of our thoughts and emotions. As we age, we find it increasingly difficult to generate enough energy to power mental activity. Worse, just like an old car leaves behind a cloud of smoke, the power source of our cells begins to produce unnecessary waste products that slowly pollute our brains. This means that mitochondrial dysfunction may underlie some of the most serious brain diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and motor neuron disease.
According to this “grand unified theory” of neurodegeneration, recharging neurons through restoration of their power plants can prolong healthy brain function. This idea has already inspired some exciting new treatments for age-related brain diseases, with multiple drug candidates under investigation. Some researchers are exploring the possibility of transplanting healthy mitochondria into damaged, aging brains to reactivate them. “If you keep replacing the parts in your car, it can last forever,” he says. claudio soto, a neurologist at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. “So what happens if we try to run this…
Source: www.newscientist.com