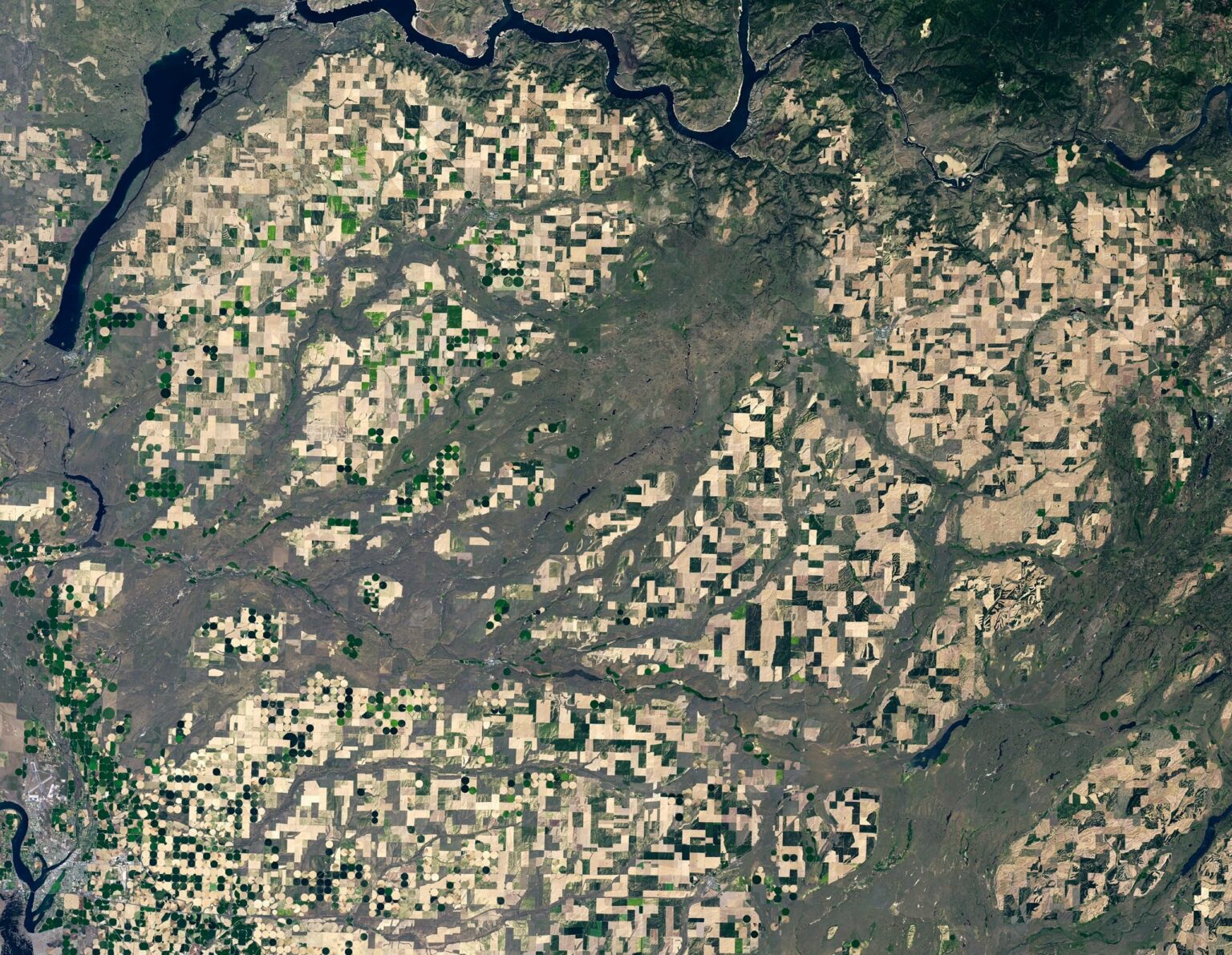
Satellite image of parts of Akaland taken on May 14, 2023 by Landsat 8’s Operational Land Imager.
Ejecta from Missoula Glacier Lake has carved out channeled skeletal lands in Washington state.
Southeastern Washington is home to miles of rolling hills and a neat grid of farmland. Dozens of crops It is grown on precious farmland on the Columbia Plateau. But in some places, undulating streaks of scoured soil interrupt a series of angular plots or center-pivot irrigated fields.
These rocky scars channeled scrubland, and they were formed in a series of dramatic floods 10,000 to 20,000 years ago. Landsat 8’s OLI (Operational Land Imager) captured the image of part of Acarland, about 120 kilometers (75 miles) west of Spokane, on May 14, 2023.
The sources of water that carved these unusual landforms remained a mystery to geologists for decades. Then they came to understand that as the Cordilleran Ice Sheet moved south during the last ice age, it formed dams along the Clark Fork River. Glacial Lake Missoula grew behind this ice dam in what is now western Montana and eventually held as much water as Lake Erie and Lake Ontario combined. Geologists estimate that: a dam was formed and broke dozens of times Over thousands of years, each breach releases up to 600 cubic miles of water across the region.
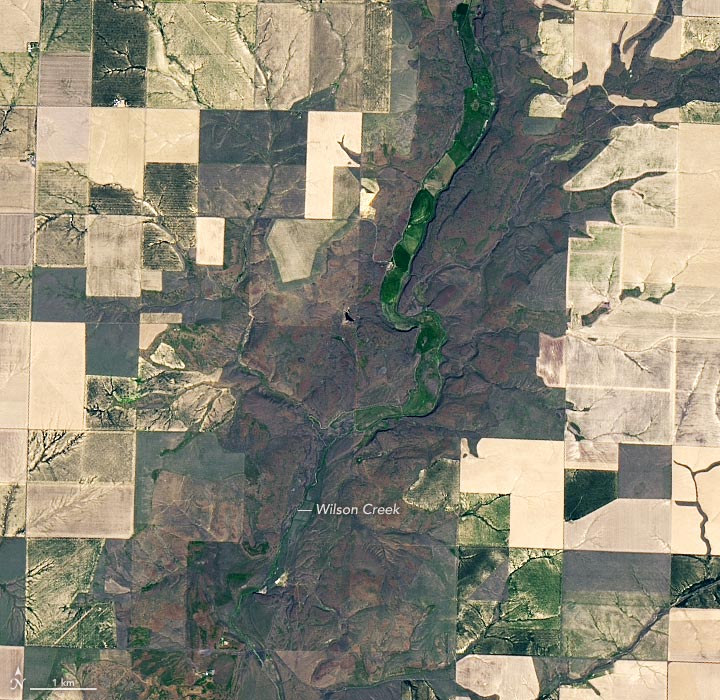
Detailed view of the image above.
Floodwaters flowed south and southwest, eventually emptying into the Columbia River. In the process, they carved grooves, potholes, and long channels known as “coulees” into the volcanic basalt bedrock. The detailed map (above) shows one of these channels and reveals the striking contrast between flood scoured areas and arable land.
The canyon shown here is small compared to the others. Grand Coulee, the largest of the Channeled Scrublands north of this scene. Completed in 1942, Grand Coulee Dam was the largest concrete structure in the world until it was surpassed by dams in South America. Itaipu Dam 1984 and China three gorges dam Established in 2006.Currently America’s largest hydroelectric facility Provides irrigation water to the Columbia Plateau.
NASA Earth Observatory imagery by Lauren Dauphin using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey.
Source: scitechdaily.com












