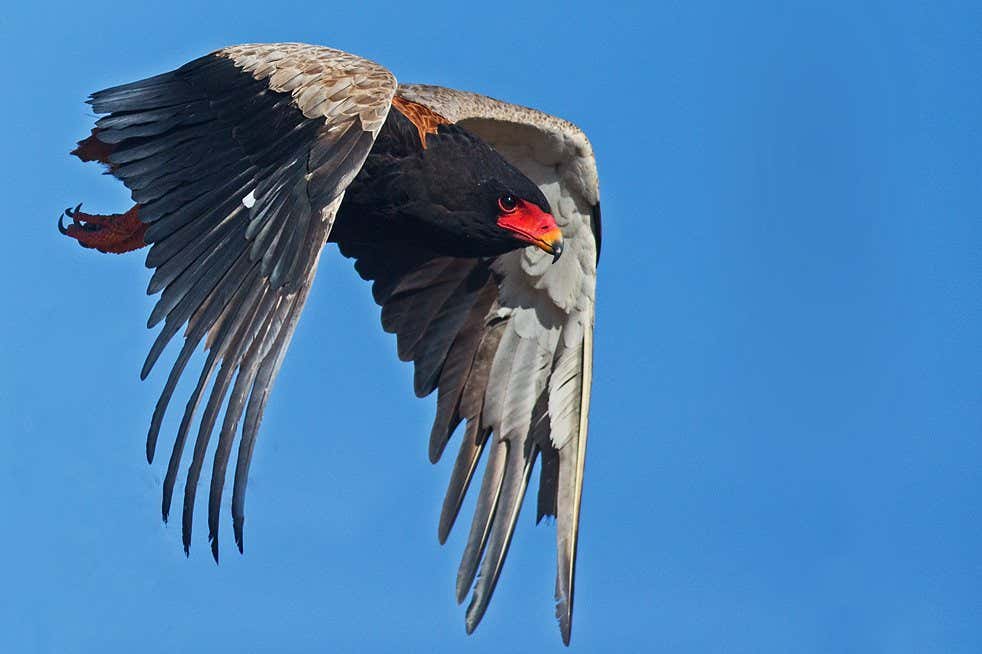
Bateleur decreased by 87% in 3 generations
Andre Botha
Dozens of African raptor species are in sharp decline, and many are now considered at risk of extinction, according to an analysis of data from across Africa.
Populations of nearly all 42 species studied have declined due to the spread of agriculture, pesticide use, poisoning by poachers, and infrastructure such as power lines that are deadly to the birds.
These include the secretary bird (sagittarius the serpent), decreased by 85 percent over three generations. Marshall Eagles (Polemaetus bellicosus), reduced by 90% on the same basis.Teratopius Exaudatus), decreased by 87 percent.

Secretary birds decline by 85% in 3 generations
Darcy Ogada
A study has found that some birds that were previously thought not to be in danger of extinction are now on the verge of extinction. For example, the African goshawk (Aquila Spirogaster) is now listed as 'least concern' by the International Union for Conservation of Nature and is estimated to have declined by 91 percent.
Some have called for the list of such species to be moved higher in the conservation rankings to reflect this change. “We definitely expect this paper to put pressure on the rest of the papers to pull it up.” [of the surveyed species now facing threats]sooner or later,” say the study authors. Darcy Ogada from the Peregrine Fund, a US-based organization.
Data was collected from more than 53,000 sightings of 42 species on approximately 100,000 kilometers of surveyed roads in Burkina Faso, Niger, Mali, Cameroon, Botswana and Kenya between 1969 and 2020.
Additional data came from the latest South African Bird Atlas project, a citizen science-led survey.
The researchers found that population declines for 42 species were more than twice as severe in unprotected areas than in protected areas, and that well-managed national parks and reserves have long-term implications for bird species. shown to be important to aid survival.
Further research is needed to understand the fate of these birds. “There is an urgent need to increase research that estimates raptor population trends based on loss of habitat for endangered species, such as forests, wetlands, and grasslands, or modeling loss and mismanagement of protected areas.” Mr. Ogata says.
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com