The newly discovered galaxy, called the Firefly Radiance, existed about 600 million years after the Big Bang and consisted of at least 10 star clusters.
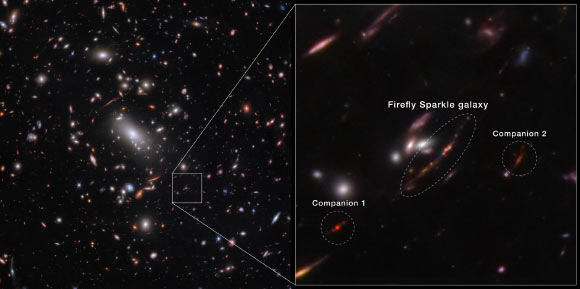
The Firefly Sparkle galaxy is in the process of gathering and forming new stars, exists about 600 million years after the Big Bang, and would weigh about the same as the Milky Way if we could turn back the clock and watch the galaxy develop . Image credits: NASA / ESA / CSA / STScI / C. Willott, NRC-Canada / L. Mowla, Wellesley College / K. Iyer, Columbia.
The most distant galaxies detected date from when the universe was about 5% of its current age.
However, the mass of these galaxies is about 10,000 times smaller than that of the Milky Way, making them difficult to observe.
The Firefly Sparkle galaxy was first observed by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, but detailed new observations by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope shed more light on its formation.
“We never thought it would be possible to resolve galaxies that existed so early in the universe into so many different components, much less that their mass would be comparable to the mass of our galaxy in the process of forming. “I never thought it would be possible to discover similarities between the two,” he said. Dr. Ramiya Moura, astronomer at Wellesley College.
“There’s so much going on inside this small galaxy, including various stages of star formation.”
Webb was able to image the Firefly Sparkle galaxy in sufficient detail for two reasons.
One is the blessings of the universe. A massive galaxy cluster in the foreground, called MACS J1423.8+2404, radically enhanced the appearance of distant galaxies through a natural effect known as gravitational lensing.
And when combined with the telescope’s specialization in high-resolution imaging in infrared light, Webb provided unprecedented new data on the contents of galaxies.
“Without the benefit of this gravitational lensing, we would not have been able to understand this galaxy,” said Columbia University astronomer Karltej Ayer.
“We knew that was expected based on current physics, but to actually witness it was surprising.”
Astronomers also observed two neighboring galaxies they named Firefly Best Friend and Firefly New Best Friend. These galaxies are located 6,000 and 40,000 light-years from Firefly Sparkle, respectively, and are smaller than the present-day Milky Way.
The authors propose that the firefly glow could be a young, gas-rich galaxy in the early stages of formation.
These show that Firefly Sparkle’s mass is concentrated in 10 star clusters, with a total mass about 10 million times the mass of the Sun.
As such, Firefly Sparkle is one of the lowest-mass galaxies to have resolved into star clusters observed at the dawn of the universe, when galaxies began to form, and its mass is similar to that of the progenitor Milky Way. is.
“It has long been predicted that galaxies in the early universe formed through continuous interactions and mergers with other smaller galaxies,” says Yoshihisa Asada, a doctoral student at Kyoto University.
“We may be witnessing this process in action.”
“We have just started using space microscopy, so this is only the first of many such galaxies that Webb will discover,” said Dr. Marcia Bradač, an astronomer at the University of Ljubljana.
“Just as we can see pollen grains on plants with a microscope, the incredible resolution of the Webb and the magnifying power of gravitational lenses allows us to see tiny pieces inside galaxies.”
“Our team is currently analyzing all the early galaxies, and the results all point in the same direction. We still don’t know much about how these early galaxies formed. .”
of study Published in a magazine nature.
_____
L. Mora others. 2024. Low-mass galaxies were formed from star clusters in the Universe 600 million years ago. nature 636, 332-336; doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08293-0
Source: www.sci.news