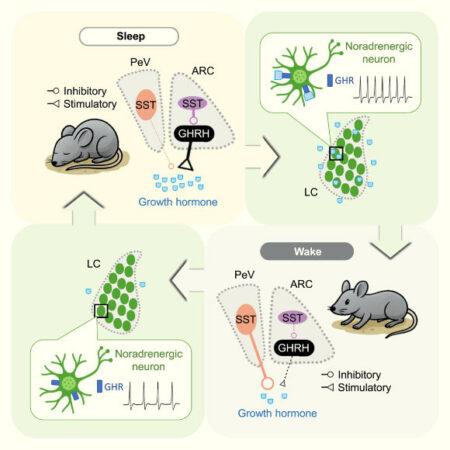
Imagine being able to visualize every aspect of our bodies, from our genes to the smallest cells that make up our organs. Scientists are now working on creating a comprehensive directory known as the Human Cell Atlas.
Think of it as a GPS for cells in the body, containing information on how cells evolve over time. This groundbreaking study, spanning 40 research papers, could potentially unravel major scientific mysteries such as bone formation, arthritis, and Crohn’s disease development.
Researchers have already gathered data on over 100 million cells from more than 10,000 individuals, with hopes of incorporating this information in the final atlas, which could potentially include billions of cells.
Professor Sarah Teichmann, the founding co-chair of the Human Cell Atlas and a researcher at the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute, stated, “This new level of insight into specific genes, mechanisms, and cell types within tissues lays the foundation for more accurate diagnosis, innovative drug discovery, and advanced regenerative medicine approaches.”
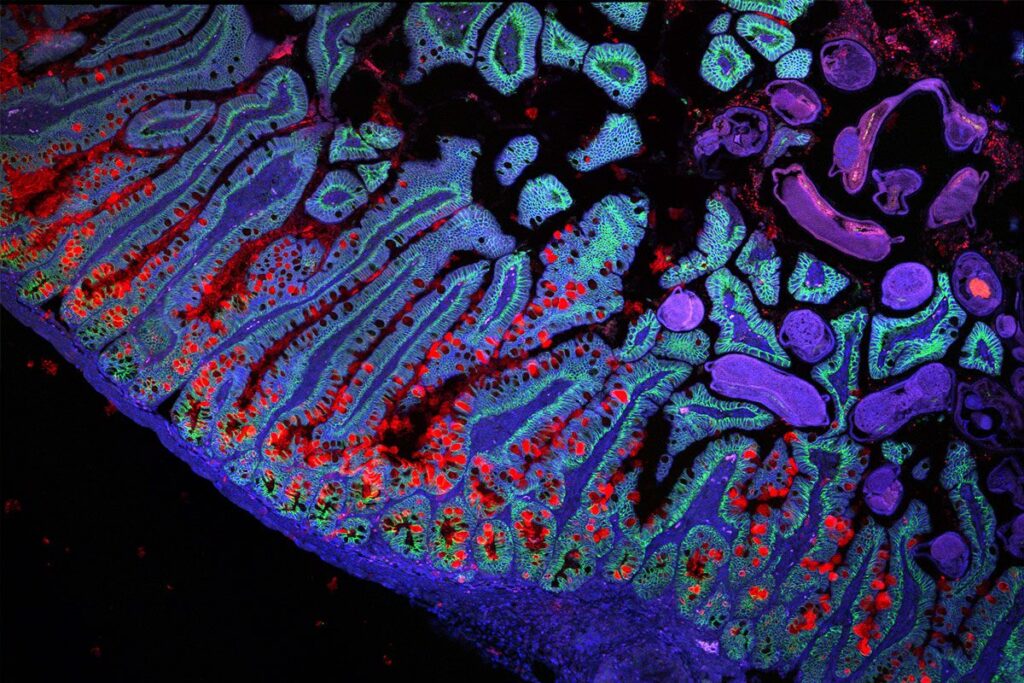
One significant milestone in the project focuses on the digestive system. By compiling data from 1.6 million cells, researchers have created an intricate map of intestinal cells, detailing their types, locations, and interactions within the body – the most detailed map of its kind.
Utilizing sophisticated techniques such as computer analysis and artificial intelligence (AI), researchers isolated individual cells and identified them, demonstrating the potential for AI in disease diagnosis.
A new approach similar to a “reverse image search” is being employed by researchers to aid in disease diagnosis, potentially revolutionizing the field.
Two striking images from the study stand out:
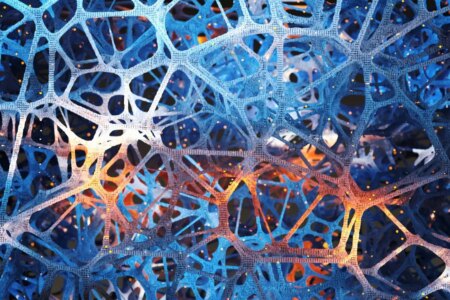
This captivating image displays a magnified view of lung tissue, shedding light on the body’s response to COVID-19.

While it may resemble an artistic beach scene, this image actually depicts the intricate structures of the small intestine, a crucial organ in the digestive process.
Read more:
Source: www.sciencefocus.com