Cocuus, a cutting-edge technology start-up headquartered in an industrial park on the outskirts of Pamplona, takes on a group of drunken tourists who willingly surrender to the sound of fate, horns and hooves during a bull run in a Spanish city. They are just as happy to embrace every bit of the clichés of their sector. A festival held every July.
Table soccer? check.lager and IPA on tap? check. Inspirational Message – Preferably an homage to Alice in Wonderland with “Before Breakfast She Believes in Six Impossible Things”? Check. How about sci-fi memorabilia, perhaps Tintin's moon rocket or Alien's xenomorph head? Check. clearly.
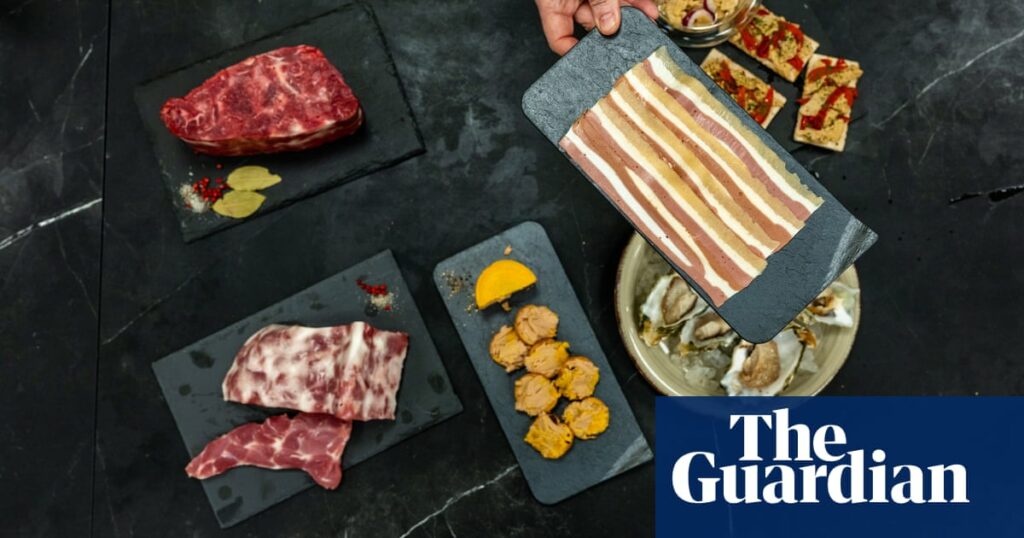
A clue as to what's different lies in the platters of oysters, tuna, foie gras, bacon, nuggets, steak and charcuterie displayed at the bar. Nothing is what it seems. Steak and pork do contain meat, but like other dishes, they are the result of years of research into “copycat foods,” culminating in the rapid burst of 3D printing.
Founded six years ago by Patxi Larumbe and Daniel Rico, Cocuus continues its loud and disruptive quest to fuse science, technology, and nutrition. It announced its existence three years ago when the duo decided to attract meat lovers in Pamplona and beyond by 3D printing steaks and posting them on social media.
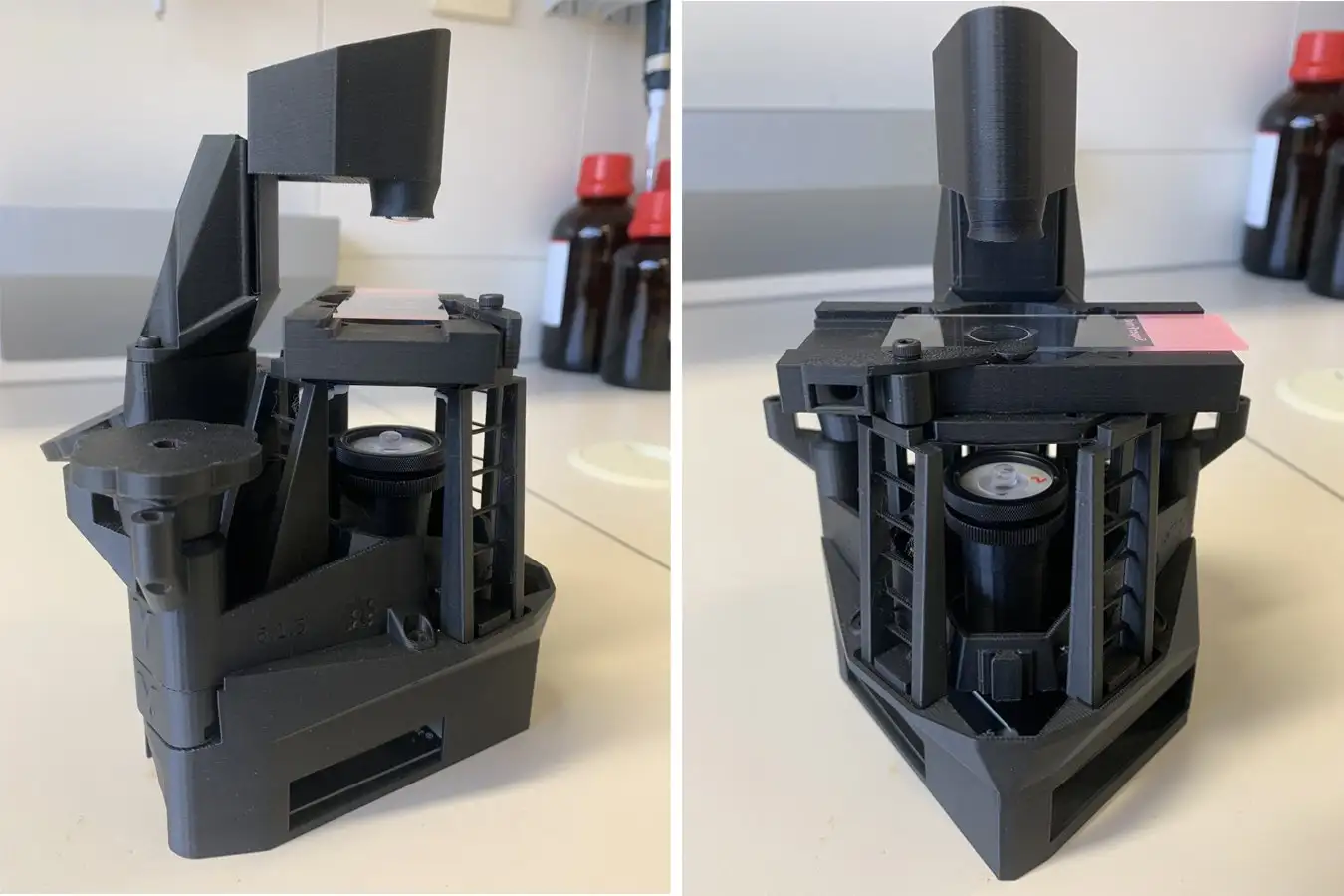
Patsi Larumbe with 3D machinery to produce shrimp. Photo: Markel Redondo/Guardian
“I knew that if I was going to print something, it had to be something that would piss people off,” says Larumbe, who quit a €100,000-a-year job in construction materials to focus on the startup.
“We knew that printing a big steak would upset a lot of people in Spain, especially in northern Spain. So we printed the steak and posted it on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. 700,000 people. We got replies. Most of them were people telling us to shove it up our butts. It was crazy and I was really happy.”
Even better, the product also attracted the attention of American food company Cargill, which is now one of Coccus' major investors. This Spanish company also specializes in formulations and machinery used in food printing, and for the past few years has designed and manufactured multi-nozzle printers that can create food products that mimic the taste and texture of meat and fish. . The hardware can also be painted on molded purees to look like a plate of chicken and chips or hake and peas, creating meals that stimulate the eyes and appetites of people with swallowing difficulties.
As befits a self-confessed bunch of sci-fi geeks, much of the inspiration comes from the transport plane that beams the crew of the USS Enterprise between the ship and the planet's surface. Larrambe said Social Media Steak is the result of experimenting with the idea of converting steak cells into data that can be teleported. After taking X-rays and cross-sectional scans of real steaks, they located the cells that make up the meat, fat, and bones, converted them into data, and entered them into a printer.
Larumbe cooks 3D vegan steaks. Photo: Markel Redondo/Guardian
“We're a group of physicists, geometry mathematicians, geeks, and Star Trek and Star Wars enthusiasts who are starting to research food,” Larumbe says. “Every food company studies things in very similar ways, using nutritionists and food technologists, and they come to very similar conclusions to existing ones. To come up with new cakes. If you get a bunch of bakers together, they'll come up with something very similar to what already exists and what we know as cake.”
But if you combine a physicist with a nutritionist, a machine maker, a baker and a comedian, he added, “you'll create a new kind of cake.”
Cocuus' bacon and foie gras are made from a rich vegetable paste, while the steaks are made with real beef from 50kg of meat that would otherwise be discarded or made into cat food when cows are slaughtered. The fat in steak marbling is made from a vegetable mixture and is much lower in saturated fat than the real thing.
Mr Larumbe exudes confidence in his products as surely as his printers extrude meat and vegetable pastes, but he also takes a swipe at many of his supposed rivals and says they've made light work of the vegan burger boom in recent years. He dismissed it as a “bubble” and pointed out the huge costs and low costs. Yields of lab-grown meat.
Cocuus' 3D printed meat steaks contain real beef. Photo: Markel Redondo/Guardian
When asked what sets his company apart in an already crowded field, he insists it's scale. Cocuus and its partner Foody's have sold 80,000 pieces of meat-free foie gras and 200,000 pieces of cholesterol-free vegan bacon since the products hit Carrefour store shelves last September. Cocius also has the production capacity to produce 1,000 tons of bacon and his 3,000 tons of foie gras annually at his factory in the city of Tudela.
“We are the first company in the world to successfully do this on an industrial scale rather than on an experimental scale,” says Larumbe.
“Secondly, our imitation is complete and has never existed before. There was a vegetarian version, but the content was bad. Thirdly, there is something fundamentally wrong here. We have scientists coming up with different formulations and technologies. All of this means we are the most advanced company in the world in this field, and one that partners with the largest international food companies. about it.”
What has the local reaction been like in areas where beef is highly revered?
Making bacon without pigs or “seeing a bunch of idiots make steaks with 3D printing” may not be appealing to Navarre's farmers, Larumbe admits. But after learning more about the company and understanding that more money could be made for the cows thanks to new technology that utilizes parts that were traditionally thrown or fed to cats, many He says people are coming.
Once again, after spending an hour or two with him, you get the impression that Larumbe doesn't really care about other people's opinions.
“Humanity progresses because of people who disagree,” he says. “There is no progress if you and I agree. We don't agree on everything.”
Source: www.theguardian.com