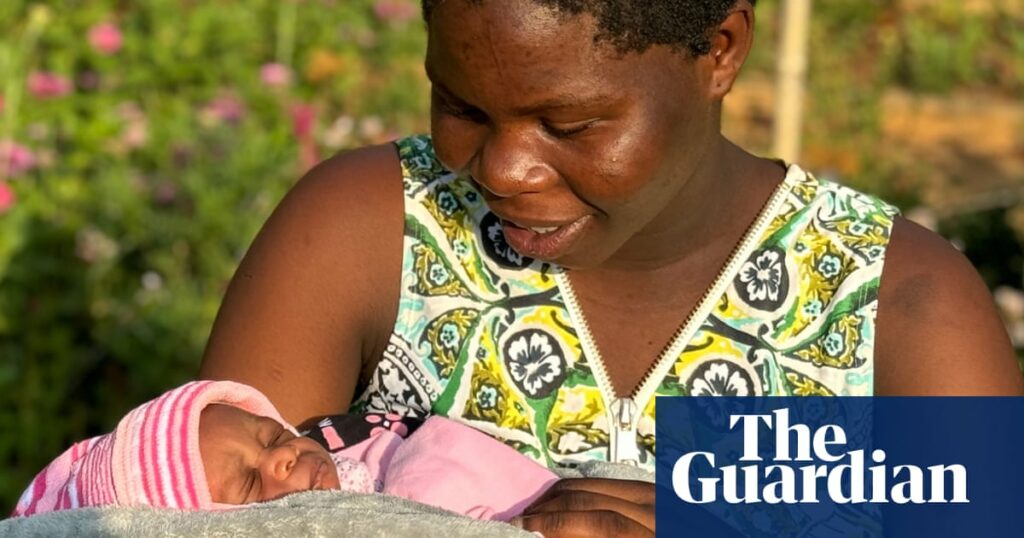
WEllen Kafamtengo felt a sharp pain in her lower abdomen and thought she might be going into labor. It was the ninth month of her first pregnancy, but she wasn’t taking any chances. With the help of her mother, the 18-year-old took a motorbike taxi and raced to a hospital in Malawi’s capital Lilongwe, a 20-minute drive away.
At Area 25 Health Center, she was told it was a false alarm and taken to the maternity ward. But when a routine ultrasound reveals that the baby is much smaller than expected at this stage of pregnancy, things quickly escalate, leading to suffocation, a condition that limits blood flow and oxygen to the baby may cause.
In Malawi, approx. 19 out of 1,000 babies Death occurs during childbirth or within the first month of birth. Childbirth asphyxia is the leading cause of neonatal death in this country and can result in brain damage to newborns with long-term effects such as developmental delays and cerebral palsy.
Doctors reclassified Ms Kafamtengo, who was expected to have a normal delivery, as a high-risk patient. Further tests using AI-powered fetal monitoring software revealed that the baby’s heart rate was slow. Stress tests revealed that the baby would not survive delivery.
Chikondi Chiweza, head of maternal and child care at Area 25 Health Center in Lilongwe, said: Photo: Provided by Halma plc
Chikondi Chiweza, the hospital’s head of maternal and child care, knew she had less than 30 minutes to deliver Kafamtengo’s baby by caesarean section. Having delivered thousands of babies in some of the city’s busiest public hospitals, she was well aware of how quickly a baby’s chances of survival can change during delivery.
Chiweza, who gave birth to Kafamtengo’s baby healthy, says the fetal monitoring program has made a huge difference to hospital births.
“[In Kaphamtengo’s case]we wouldn’t have realized what we did until later or as a stillborn baby,” she says.
Software donated by a birth safety technology company Perigen Through a partnership with the Malawi Ministry of Health, Texas Children’s Hospitaltracks your baby’s vital signs during delivery, giving clinicians early warning of abnormalities.
Since it began using the system three years ago, the number of stillbirths and neonatal deaths at the center has fallen by 82%. It is the only hospital in the country that has introduced this technology.
“The period around birth is the most dangerous for mothers and babies,” says Jeffrey Wilkinson, an obstetrician at Texas Children’s Hospital who leads the program. “Most deaths can be prevented by ensuring the baby’s safety during the birth process.”
AI monitoring systems require less time, equipment, and skilled staff than traditional fetal monitoring methods, making them essential for hospitals in low-income countries such as Malawi, which face severe health worker shortages. Routine fetal monitoring often relies on a doctor performing routine tests. This means that while the AI-assisted program provides continuous, real-time monitoring, important information may be missed during the interval. Traditional tests also require doctors to interpret raw data from various devices, which can be time-consuming and error-prone.
Area 25’s maternity ward handles approximately 8,000 births annually with a staff of 80 physicians. While only about 10% are trained to perform traditional electronic monitoring, most can detect abnormalities using AI software, helping doctors recognize higher-risk or more complicated births. Masu. Hospital staff also say that the use of AI has standardized key aspects of obstetric care in the clinic, such as interpreting fetal health status and deciding when to intervene.
Kafamutengo, who is excited to become a new mother, believes that doctors’ intervention may have saved her baby’s life. “They realized early enough that my baby was suffering and were able to take action,” she said as she held her son, Justice.
Doctors at the hospital hope the technology will be introduced to other hospitals in Malawi and across Africa.
“AI technology is being used in many fields, and saving the lives of babies is no exception,” Chiweza said. “We can really close the gap in the quality of care available to underserved populations.”
Source: www.theguardian.com