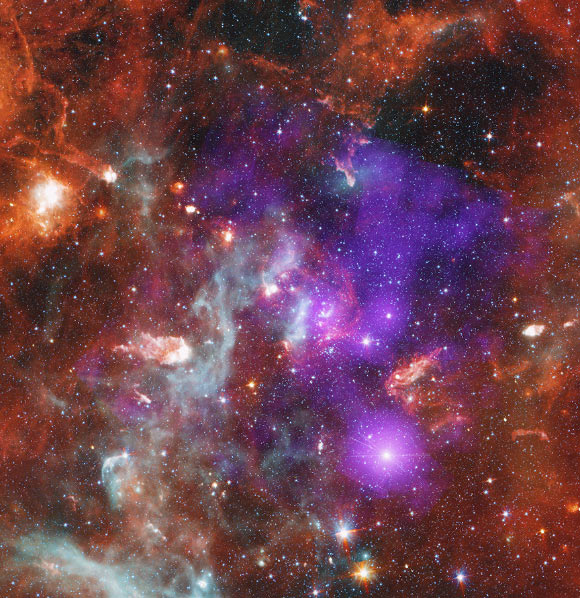
Cygnus OB2 is the giant young stellar association closest to the Sun.
In this new composite image, Chandra data (purple) shows the diffuse X-ray emission and young stars of Cygnus OB2, along with infrared data (red, green, blue, cyan) from NASA's now-retired Spitzer Space Telescope reveals young stars. And it creates cold dust and gas throughout the region. Image credits: NASA / CXC / SAO / Drake others. / JPL-California Institute of Technology / Spitzer / N. Walk.
At a distance of approximately 1,400 parsecs (4,600 light years), Cygnus OB2 It is a huge young body closest to the Sun.
It contains hundreds of double stars and thousands of low-mass stars.
Dr. Mario Giuseppe Guarcero of the National Institute of Astrophysics, Dr. Juan Facundo Albacete Colombo of the University of Rio Negro, and colleagues used NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory to study various regions of Cygnus OB2. observed.
This deep observation mapped the diffuse X-ray glow between the stars and also provided an inventory of young stars within the cluster.
This inventory was combined with other inventories using optical and infrared data to create the best survey of young stars within the association.
“These dense stellar environments are home to large amounts of high-energy radiation produced by stars and planets,” the astronomers said.
“X-rays and intense ultraviolet radiation can have devastating effects on planetary disks and systems that are in the process of forming.”
The protoplanetary disk around the star naturally disappears over time. Part of the disk falls onto the star, and some is heated by X-rays and ultraviolet light from the star and evaporates in the wind.
The latter process, known as photoevaporation, typically takes 5 million to 10 million years for an average-sized star to destroy its disk.
This process could be accelerated if there is a nearby massive star that produces the most X-rays and ultraviolet light.
researchers Found Clear evidence that protoplanetary disks around stars actually die out much faster when they approach massive stars that produce large amounts of high-energy radiation.
Also, in regions where stars are more densely packed, the disk dies out faster.
In the region of Cygnus OB2, which has less high-energy radiation and fewer stars, the proportion of young stars with disks is about 40%.
In regions with higher-energy radiation and more stars, the proportion is about 18%.
The strongest influence, and therefore the worst location for a star to become a potential planetary system, is within about 1.6 light-years of the most massive star in the cluster.
In another study, the same team I looked into it Characteristics of the diffuse X-ray emission of Cygnus OB2.
They discovered that the high-energy, diffuse radiation originates from regions where winds of gas blown from massive stars collide with each other.
“This causes the gas to become hot and generate X-rays,” the researchers said.
“The low-energy release is likely caused by gas within the cluster colliding with gas surrounding the cluster.”
_____
MG Guarcero others. 2024. Photoevaporation and close encounters: How does the environment around Cygnus OB2 affect the evolution of the protoplanetary disk? APJS 269, 13; doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/acdd67
JF Albacete vs Colombo others. 2024. Diffuse X-ray emission in the Cygnus OB2 coalition. APJS 269, 14;doi: 10.3847/1538-4365/acdd65
Source: www.sci.news