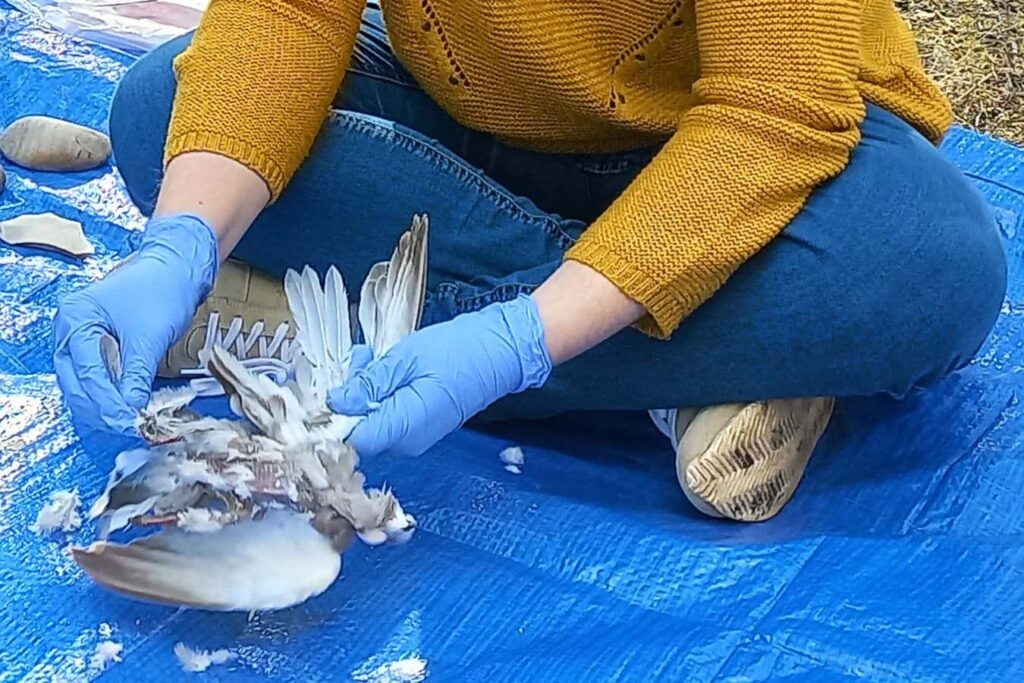
A researcher plucks the feathers of a bird as part of an experiment to investigate Neanderthal cooking techniques.
Mariana Navaiz
To learn more about Neanderthal culinary talents, archaeologists cooked five wild birds using only fire, their hands, and stone tools. The experiment shows that our ancient relatives needed significant manual skill to use a flint blade to butcher an animal without injuring themselves.
Neanderthals lived in Europe and Asia until about 40,000 years ago. Hearths have been found at many of their sites, and there is evidence that they hunted large animals such as elephants and cave lions.
Mariana Navaiz Researchers at the Catalan Institute of Human Palaeoecology and Social Evolution in Tarragona, Spain, say that by recreating ancient activities such as cooking and butchering using tools available at the time, scientists can gain insight into how prehistoric humans lived.
She and her colleagues wanted to better understand archaeological bird remains associated with Neanderthals that date back about 90,000 years ago and were found in deposits in Portugal.
The team selected five birds that had died at a wildlife rehabilitation center in Portugal and were similar in size and species to those found at the archaeological site.Crow), Turtledove(Columba Palumbus) and two European collared doves (Streptopelia decaoctoThe tools used in the experiment were pieces of flint prepared by students of stone tool technology.
All five birds were plucked by hand. The crow and pigeon were butchered raw, while the remaining three were roasted over charcoal. The cooked birds were easily butchered without stone tools, but the raw birds required considerable effort using a flint blade.
“Paleolithic knives were certainly very sharp and required careful handling,” Navais says. “The precision and effort required to use these tools without injuring oneself highlights the practical challenges Neanderthals would have faced in their everyday food processing activities.”
Once the dissection was complete, the researchers prepared the bones and analyzed them for distinctive marks caused by stone tools and fire, as well as identifying wear marks from flint tools.
The burn marks and tool marks were then compared to Neanderthal food remains found at the archaeological sites of Fighiera Brava and Oliveira in Portugal, where bird bones with burn marks and cut marks matched the team’s reconstruction, Navaís said.
“Our experimental studies demonstrate that flaked raw birds display characteristic cut marks, especially around tendons and joints, while roasted birds display burn marks and increased brittleness leading to fractures,” she says. “These findings help distinguish between human-induced modifications and those caused by natural processes or other animals, such as trampling or the activity of rodents, raptors and carnivores.”
Neanderthals were skilled enough to capture and prepare small, fast-moving animals like birds, Navais said. “This study highlights the cognitive capabilities of Neanderthals and demonstrates their ability to capture and prepare small, fast-moving prey like birds, challenging previous ideas that they were incapable of such complex tasks.”
Sam Lin Researchers at the University of Wollongong in Australia say experimental archaeology is like reverse engineering, comparing what happens in modern samples with archaeological material to try to interpret what happened in the past.
In this case, one of the main findings is that cooked birds don’t require tools to prepare them for eating, which means some bones may not necessarily bear tool marks. “They learned that you just need to tear apart a cooked wild bird, just like we do when we eat barbecued chicken,” Lin said.
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com