Early galaxies are dominated by bright galaxy clusters, which are larger and more massive than the local Universe. Star formation activity can be strongly influenced and even halted by many processes that are directly related to the environment in which galaxies exist. Ram pressure stripping, the removal of interstellar gas from the disk of star-forming galaxies by hydrodynamic interaction with the hot intergalactic medium, is one such process that It is thought to have a strong influence on the galaxy population. Groups, especially clusters.
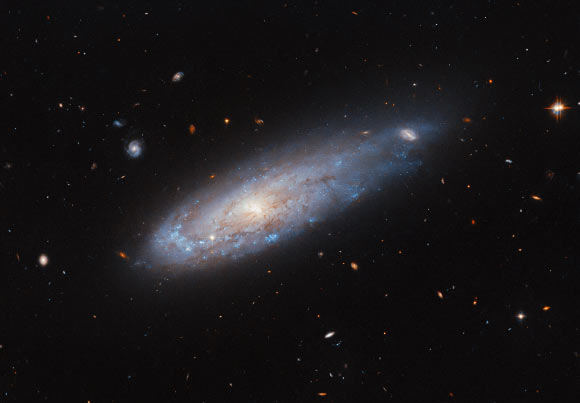
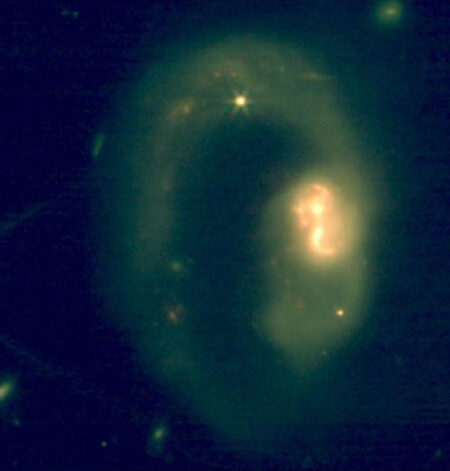
This Hubble image shows spiral galaxy IC 3225 with Ram pressure removed. Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / M. Sun.
IC 3225 is a spiral galaxy located approximately 100 million light years away in the constellation Virgo.
Also known as LEDA 40111 or UGC 7441, discovered It was announced on November 4, 1899 by German astronomer Arnold Schwassmann.
“IC 3225 looks strikingly like it was fired from a cannon, hurtling through space like a comet with a tail of gas streaming from the disk behind it,” Hubble astronomers said in a statement.
“IC 3225 is one of more than 1,300 members of the Virgo cluster, so the galaxy's location suggests several causes for this active scene.”
“While the density of galaxies within the Virgo cluster creates a rich field of hot gas between them, the so-called intracluster medium, the extreme mass of this cluster also allows for some extremely There are galaxies that orbit around the center in fast orbits.”
“Collision into thick intracluster material, especially near the center of a galaxy cluster, places enormous collision pressures on the moving galaxy, stripping the gas from the moving galaxy.”
“Although IC 3225 is currently not very close to the center of the cluster, astronomers suspect that it has undergone such ram pressure removal in the past,” the researchers noted.
“This galaxy looks as if it has been affected by this. One side of the galaxy is compressed and there is significantly more star formation at this leading edge, while the other end is misshapen. Masu.”
“Being in such a crowded region, a close call with another galaxy may have pulled IC 3225 and created this shape.”
“The sight of this distorted galaxy is a reminder of the incredible forces at work on an astronomical scale that move and reshape entire galaxies.”
This new image of IC 3225 consists of observations from. Hubble's advanced survey camera (ACS) in the near-infrared and optical portions of the spectrum.
Two filters were used to sample different wavelengths. Color is obtained by assigning different hues to each monochromatic image associated with an individual filter.
Source: www.sci.news