Humanity has always dreamed of traveling beyond our solar system to the stars, but the vastness of the universe has kept us grounded. Our closest star, Proxima Centauri, is a staggering 4.24 light years away, which is too far for us to wait patiently.
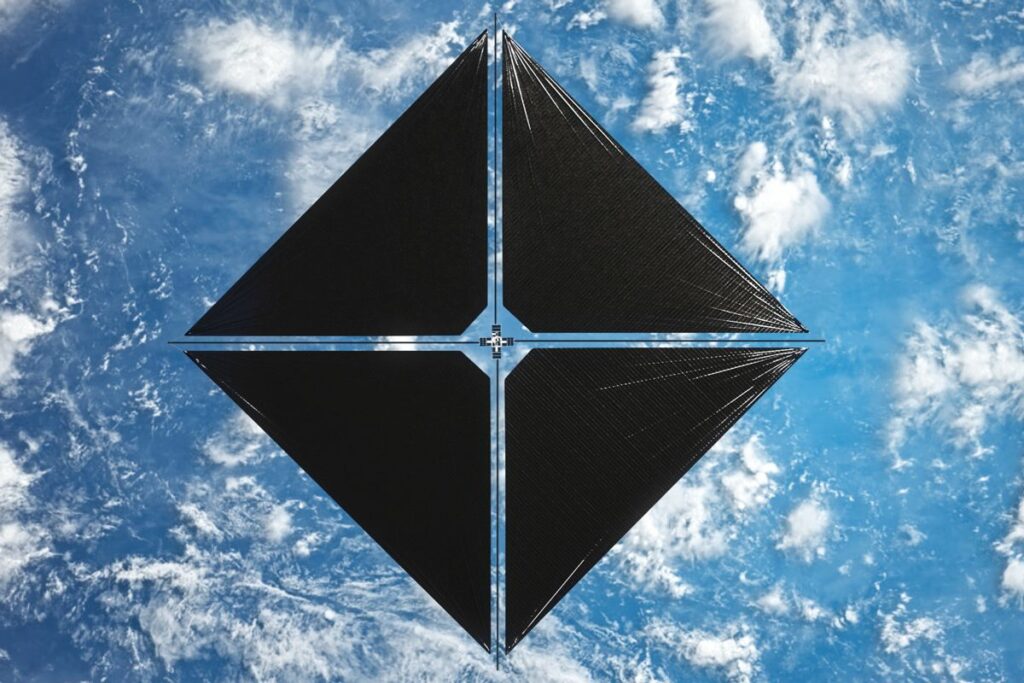
Recently, on April 23, NASA launched the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System from New Zealand, a system that uses lightweight sails to propel spacecraft instead of traditional rockets. This development has excited both experts and science fiction fans, as it opens up possibilities for long-distance space travel.
How solar sail works
Instead of using thrusters and fuel like traditional spacecraft, solar sail systems use reflective sails to absorb momentum from photons emitted by the sun. This technology enables spacecraft to gain acceleration without the limitations of fuel. In space, where there is no air resistance, a slight push from the sun is all that’s needed for propulsion.
Solar sails operate similar to sailing ships, utilizing the momentum of photons for movement. By harnessing the sun’s energy, spacecraft can travel far distances at manageable speeds.
How fast can an interstellar probe travel with a solar sail?
The speed of a solar sail system depends on factors like the size of the sail, spacecraft mass, and distance from the sun. With creative maneuvers like slingshot maneuvers and potential laser boosts, spacecraft using solar sails can achieve speeds close to 20% of the speed of light.
Will humanity ever be able to sail to another planet?
Potentially, solar sail technology could pave the way for human interstellar travel in the future. However, there are challenges, such as sustaining long-term missions for generations and addressing relativistic effects caused by near-light speed travel.
What exactly is NASA's solar sail mission?
NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System is a demonstration of solar sail technology that aims to test a new lightweight boom made of flexible materials. The mission involves a CubeSat deploying an 80 square meter sail in orbit to gather data for future solar sail missions.
About our experts
patrick johnson is an associate professor at Georgetown University with expertise in quantum mechanics. He authored the book “Star Wars Physics” and has contributed to scientific journals like Physical Review.
Source: www.sciencefocus.com