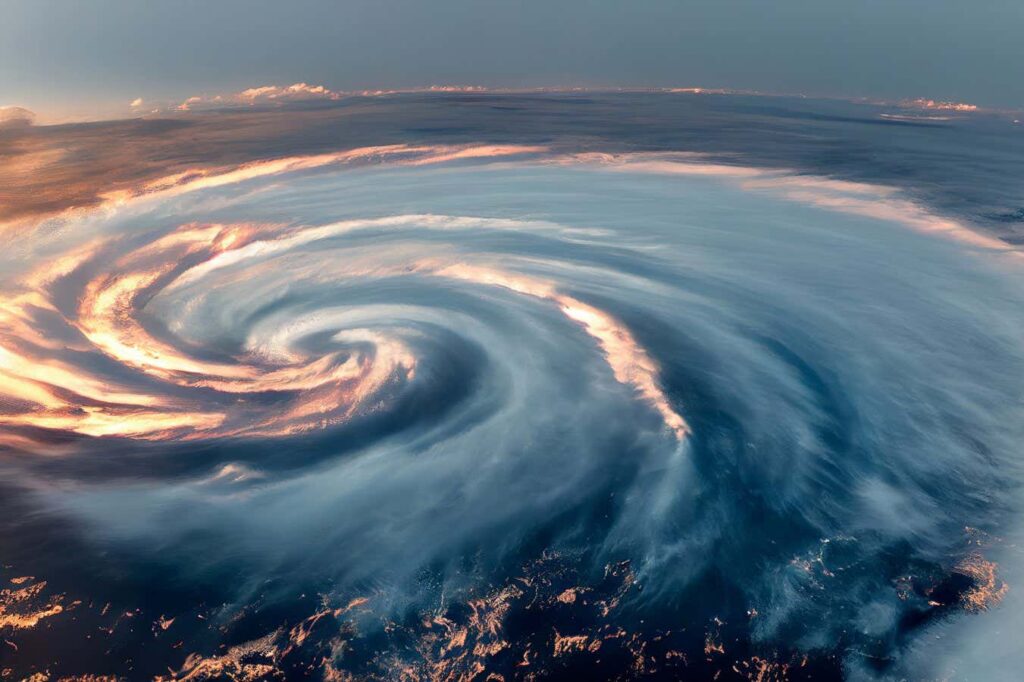
Satellite image of Typhoon Surigae over the Pacific Ocean in 2021
European Union/Copernicus Sentinel-3 images
In the past decade, five tropical cyclones have recorded wind speeds strong enough to be classified as Category 6 storms. Analysis suggests hurricane sizes may need to be updated as rising temperatures strengthen storms.
If carbon emissions continue at their current pace, a “Category 7” storm is even possible. 'It's certainly possible in theory if we keep warming the planet,' says climate scientist james cossin at the First Street Foundation, a nonprofit research organization in New York.
Officially, there is no such thing as a Category 6 or Category 7 hurricane. According to the Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale used by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) in the United States, storms with sustained wind speeds of 252 kilometers per hour or higher are categorized as Category 5.
But as the wind speeds of the strongest storms increase, Kossin and his colleagues say using this scale becomes increasingly problematic. michael wehner That's because a study at California's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory does not convey the increased risk posed by increasingly severe storms.
“The situation is bad and it's getting worse,” Kossin said. “As the climate changes, these storms will become stronger.”
They say there are three pieces of evidence that global warming is causing the wind speeds of the strongest storms to increase. First, the basic theory of hurricanes as a type of heat engine says that a hotter world should produce stronger storms.
Second, high-resolution climate models produce storms with faster winds as the Earth's temperature rises.
And finally, the real-world storm is getting stronger. Of the 197 Category 5 tropical cyclones between 1980 and 2021, half occurred in the 17 years ending in 2021, with the five fastest occurring in the last nine years of this period. It occurred on.
If the Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale were expanded to rank storms with wind speeds over 309 km/h as Category 6, all five of these storms would fall into that category. The five are Typhoon Haiyan in 2013, Hurricane Patricia in 2015, Typhoon Meranti in 2016, Typhoon Goni in 2020, and Typhoon Surigae in 2021.
However, Cossin and Wehner are not suggesting that the NHC formally adopt the Category 6 definition. Cossin says using a scale based on wind speed is fundamentally flawed, given that flooding and storm surges can pose a greater threat to life and buildings. .
Instead, they believe the NHC needs to implement an entirely new system to better communicate the overall risk posed by the storm. For example, 2008's Hurricane Ike was a massive storm that caused massive flooding and damage, but Kossin said it was only a Category 1 or 2 storm when it made landfall in the United States.
kelly emmanuel at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology agree that a new scale is needed. “While I think it's important to recognize that hurricane intensity is increasing, we should also point out that most of the damage, injuries, and loss of life from hurricanes comes from water, not wind.” he says.
“I have been an advocate of replacing the venerable but outdated Saffir-Simpson scale with a new scale that reflects the totality of risk from a particular storm,” Emanuel says.
Another hurricane expert, Jeff Masters, now semi-retired, doesn't think the NHC intends or should change the Saffir-Simpson scale. “But it's important to understand how devastating these new superstorms could be, so talking about a hypothetical Category 6 storm is a valuable communications strategy for policymakers and the public. ” he says.
Masters said wind damage increases exponentially with wind speed, with a Category 6 storm with wind speeds of 314 km/h causing four times more damage than a Category 5 storm with wind speeds of 257 km/h. It is said that there is a possibility.
topic:
- climate change/
- Abnormal weather
Source: www.newscientist.com