by
Recent research reveals a new approach that exploits persistent homology to improve stock market volatility prediction. This method has improved the accuracy of various predictive models and has significantly advanced topology and financial integration. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
In a new study published in Journal of Finance and Data Scienceresearchers at Han University of Applied Sciences International School of Business in the Netherlands, have introduced topological tail dependence theory, a new methodology for predicting stock market volatility during turbulence.
“This research bridges the gap between the abstract field of topology and the real world of finance. What’s really interesting is that this combination will help us better understand and predict stock market behavior during turbulent times. “We now have a powerful tool to do this,” said Hugo Gobat-Souto, sole author of the study.
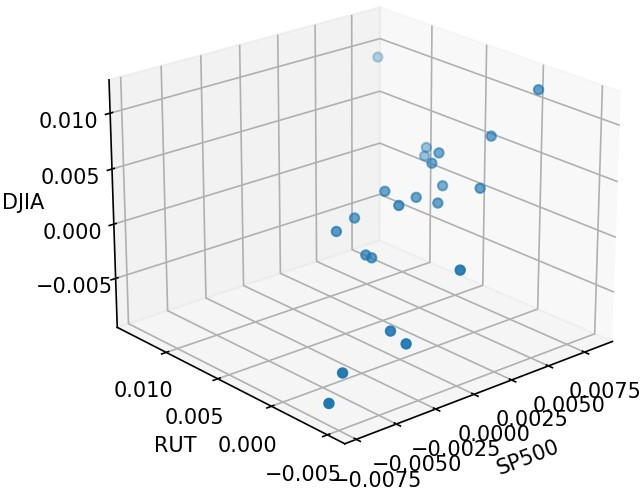
Since the difference in the average distance of normalized stock returns for two different periods is higher than the average distance in normal times than in the preceding and subsequent periods, defining a threshold to be used in normal times can help reduce the difference in periods of financial turmoil. can be used as an indicator to predict. A turbulent time. Nevertheless, a problem with this approach is the fact that the average distance of normalized price returns suffers from the curse of dimensionality and cannot detect nonlinear and complex relationships in the data. The curse of dimensionality that the average distance of normalized stock returns suffers from is that the number of dimensions (stocks in this case) tends to be infinite, so the distance between any point (say A and B) and the other The distance between points (such as A and C) approaches 1. As a result, the average distance becomes meaningless. On the other hand, his implementation of PH information via Persistent Landscape’s WD or L^n norm does not have these problems. Therefore, this is the reason for the successful introduction of PH information in recent studies and the selection of PH information in this study. Above is his 3D scatter plot from December 16, 2019 to January 16, 2020 (regular period). Credit: Hugo Gobato Souto
Enhance financial forecasting with persistent homology
By incorporating persistent homology (PH) information through empirical testing, Souto Accuracy Leveraging nonlinear and neural network models to predict stock market volatility during turbulent periods.
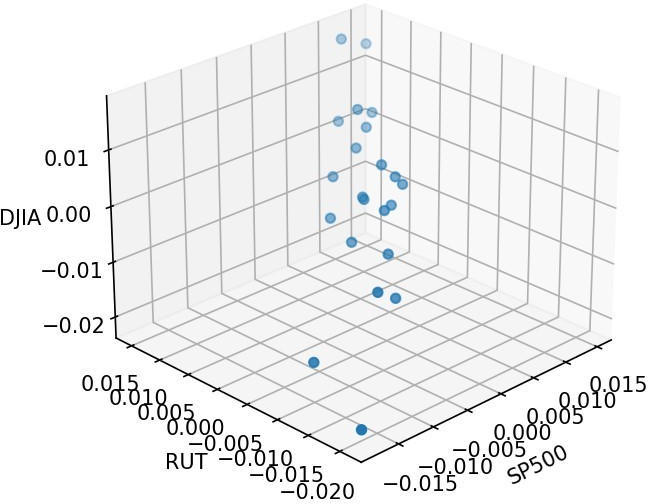
3D scatter plot from January 17, 2020 to February 19, 2020 (first period). Credit: Hugo Gobato Souto
“These findings signal a major shift in the world of financial forecasting, providing more reliable tools for investors, financial institutions and economists,” Sout added.
In particular, this approach avoids dimensionality barriers and is particularly useful for detecting complex correlations and nonlinear patterns that are often difficult with traditional methods.
“It was interesting to observe that forecast accuracy consistently improved, especially during the 2020 crisis,” Souto said.
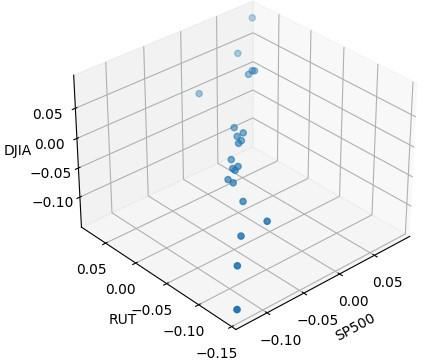
3D scatter plot from February 20, 2020 to March 23, 2020 (turbulent period) Credit: Hugo Gobato Souto
Broad implications and future directions
The findings are not limited to one particular type of model. It spans a variety of models, from linear models to nonlinear models and even advanced neural network models. These discoveries open the door to improved overall financial forecasting.
“This discovery confirms the validity of the theory and encourages the scientific community to delve deeper into this exciting new intersection of mathematics and finance,” Souto concluded.
References: “Topological tail dependence: Evidence from forecasting realized volatility” by Hugo Gobato Souto, October 14, 2023. Journal of Finance and Data Science.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jfds.2023.100107
Source: scitechdaily.com












