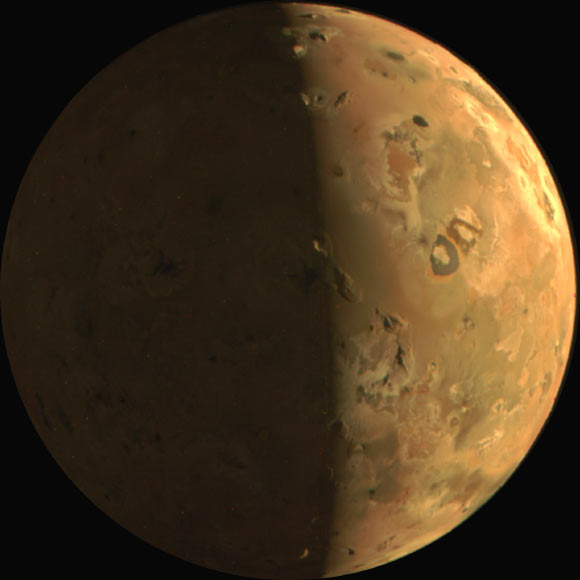
The JunoCam instrument aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft imaged Io, the most geologically active object in the solar system, on February 3, 2024, from a distance of approximately 7,904 km (4,911 miles) . Image credit: NASA/SwRI/MSSS.
Io is the innermost of Jupiter's four Galilean moons and the fourth largest moon in the solar system.
Its diameter is about 3,630 km (2,556 miles), making it only slightly larger than our moon.
It is the only place in the solar system other than Earth that is known to have volcanoes spewing hot lava like those on Earth.
Io has over 400 active volcanoes, which are caused by tidal heating. This is the result of a gravitational tug of war between Jupiter's gravity and the small but precisely timed gravitational pulls from Europa and Ganymede.
The moon's yellow, white, orange, and red colors are produced by sulfur dioxide, frost on its surface, elemental sulfur, and various sulfur allotropes.
The volcano was first discovered on the island of Io in 1979, and since then studies using NASA's Galileo spacecraft and ground-based telescopes have shown that eruptions and lava fountains occur constantly, forming rivers and lakes of lava. Masu.
Only 13 large eruptions were observed between 1978 and 2006, in part because fewer astronomers were scanning the moon on a regular basis.

The JunoCam instrument aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft imaged Io on December 30, 2023, from a distance of approximately 5,857 km (3,639 miles). Image credit: NASA/SwRI/MSSS.
NASA's Juno spacecraft has been monitoring Io's volcanic activity from distances ranging from about 11,000 km (6,830 miles) to more than 100,000 km (62,100 miles), providing the first view of the moon's north and south poles .
On December 30, 2023, Juno came within approximately 1,500 km of Io's surface. The orbiter made her second close flyby of the Moon on February 3, 2024.
The second flyby mainly flew over Io's southern hemisphere, but previous flybys flew over Io's northern hemisphere.

Juno captured two plumes rising above Io's horizon on February 3, 2024. These plumes were emitted from two vents from one giant volcano, or from two volcanoes located close to each other. The JunoCam instrument photographed the plume from a distance of approximately 3,800 km (2,400 miles). Image credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech / SwRI / MSSS / Andrea Luck.
“We investigate the source of Io's massive volcanic activity, whether there is a magma ocean beneath its crust, and the importance of tidal forces from Jupiter that are relentlessly squeezing this beleaguered moon. doing.”
“There are active plumes, high mountain peaks with distinct shadows, and evidence of lava lakes, some of which look like islands.”
Starting in April 2024, Juno will conduct a series of occultation experiments that will use Juno's gravity science experiments to investigate the composition of Jupiter's upper atmosphere. This provides important information about the planet's shape and internal structure.
Source: www.sci.news