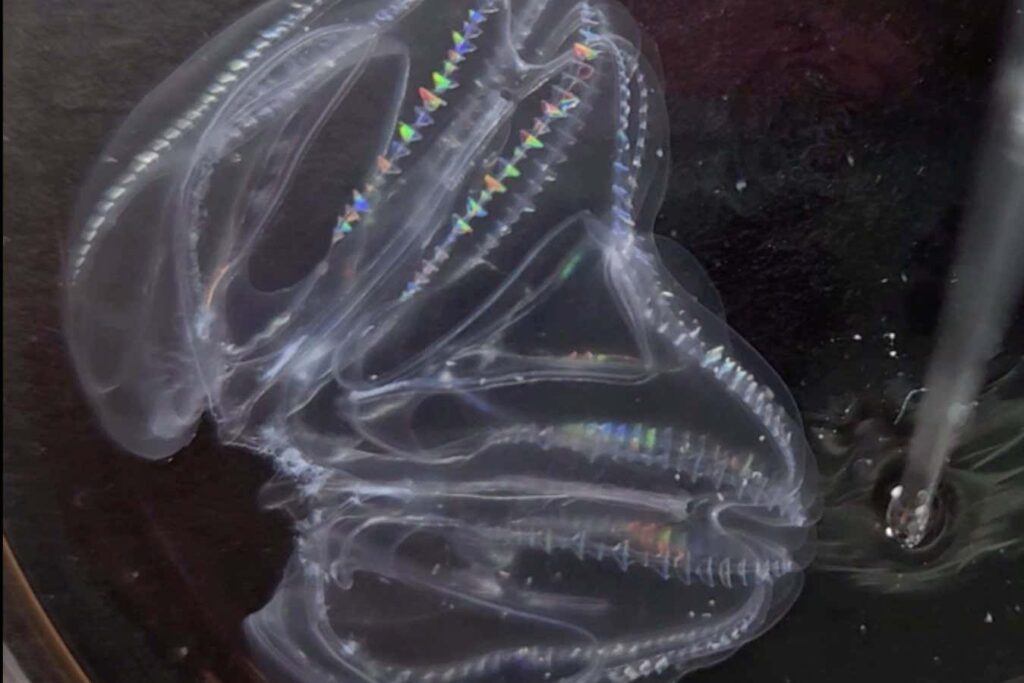
A shimmering sea creature known as a comb jelly exhibits incredible abilities. Despite being injured, two comb jellies can fuse into one body without experiencing tissue rejection, unlike other animals. Moreover, their nervous systems merge, and their digestive tracts combine to share food.
This discovery could assist researchers in understanding how the immune system evolved to differentiate an organism’s own tissues from those of another organism, as well as shed light on the evolution of the nervous system.
Although commonly referred to as comb jellies or ctenophores, they are distinct from jellyfish due to their unique body structures. These creatures are the most ancient beings to have branched off from the common ancestor of all animals, making them a captivating subject for scientists studying early animal evolution. Their nervous system, composed of interconnected neurons forming a continuous network, sets them apart from other animals.
While studying the vibrant combs of ctenophores, specifically Mnemiopsis leidii, at the University of Exeter in the UK, researcher Kei Shirokura noticed a unique specimen with two posterior ends and apical organs. This prompted further investigation.
Through experimentation involving cutting out pieces from unrelated individuals and pairing them together, Shirokura discovered that in most cases, the two bodies seamlessly merged into one within hours. The absence of tissue rejection suggested a lack of xenorecognition, indicating an inability to distinguish between self and non-self.
When prodded, the fused body responded collectively, demonstrating complete integration of the nervous systems. Additionally, the digestive tracts fused, allowing shared food consumption through a single entry point.
This groundbreaking discovery raises questions about when animals developed heterogeneous cognition and the mechanisms behind neural network formation and information processing. Similarly, ctenophores possess the ability to revert from adulthood to a larval-like stage under certain conditions, hinting at a common ancestral characteristic shared among animals.
The potential applications of ctenophores in understanding biological processes like tissue rejection, regeneration, and aging, which are relevant to human health, make them a valuable model for future research.
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com