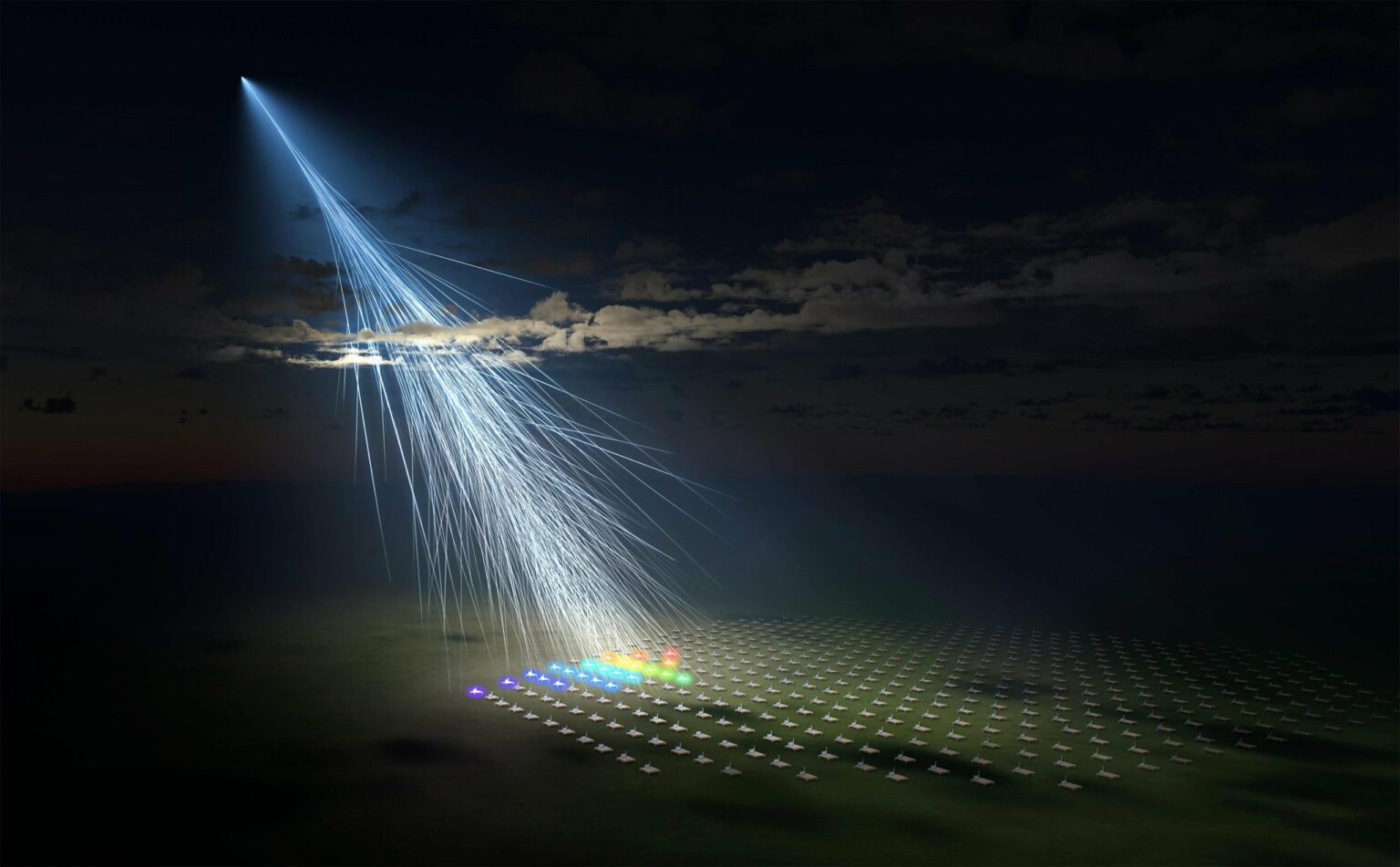
An artist’s illustration of an extremely high-energy cosmic ray, named the “Amaterasu particle,” observed by the surface detector array of the Telescope Array experiment.Credit: Osaka Metropolitan University/L-INSIGHT, Kyoto University/Ryuunosuke Takeshige
A groundbreaking detection of extremely high-energy cosmic rays by a telescope array experiment points to a void in the universe and casts doubt on current theories about the origin and high-energy physics of cosmic rays. It raises questions about its source.
Discovery of an exceptional extraterrestrial particle
Researchers involved in the telescope array experiment announced that they had detected cosmic rays with unusual energy. This particle originates outside our galaxy and has an incredible energy level of more than 240 exaelectronvolts (EeV). Despite this remarkable discovery, its exact source remains elusive, as its direction of arrival does not point to any known celestial body.
The mystery of ultra-high energy cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are subatomic charged particles that come from space, and ultra-high energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) are a rare and extremely powerful type. These UHECRs have energies in excess of 1 EeV, which is about a million times the energy reached by man-made particle accelerators. These are thought to originate from the most energetic phenomena in the universe, such as black holes, gamma-ray bursts, and active galactic nuclei. However, its exact physics and acceleration mechanisms are still not fully understood. These high-energy cosmic rays occur infrequently, estimated at less than one particle per square kilometer per century, making their detection a rare event and requiring instruments with large collection areas. .
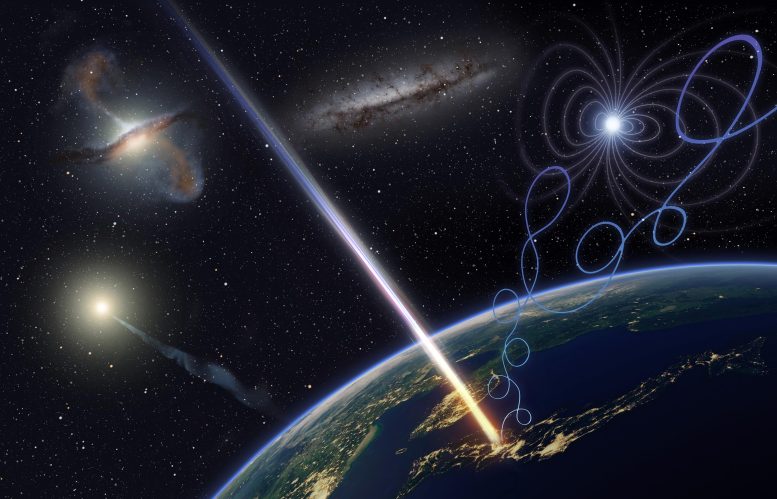
An artist’s illustration of ultra-high energy cosmic ray astronomy, which elucidates highly energetic phenomena as opposed to weak cosmic rays that are affected by electromagnetic fields.Credit: Osaka Metropolitan University/Kyoto University/Ryuunosuke Takeshige
A unique discovery of telescope arrays
The Telescope Array (TA) experiment, a large-scale surface detector array in Utah with an effective detection area of 700 square kilometers, successfully detected UHECR on May 27, 2021 at a breakthrough energy of approximately 244 EeV.
Given the very high energy of this particle, it should experience only a relatively small deflection by the foreground magnetic field, and therefore its direction of arrival should be expected to be more closely correlated with its source. Researchers point out that there is. However, our results show that the direction of arrival does not indicate an obvious source galaxy or other known objects that could be potential sources of UHECRs.
Instead, its direction of arrival points to a cavity in the large-scale structure of the universe, a region where galaxies are almost absent. Scientists believe this indicates a much larger magnetic deflection than predicted by galactic magnetic field models, an unidentified source in the local extragalactic neighborhood, or an incomplete understanding of the high-energy particle physics involved. This suggests that there is a possibility that
For more information on this discovery, see:
Reference: “Extremely high-energy cosmic rays observed by surface detector arrays”*†, RU Abbasi, MG Allen, R. Arimura, JW Belz, DR Bergman, SA Blake, BK Shin, IJ Buckland, BG Cheon, Tetsuya Fujii, Kazuya Fujisue, Kazuya Fujita, Masaki Fukushima, GD Furlich, ZR Gerber, N. Globus, Kazuto Hibino, Tatsuya Higuchi, Kazuya Honda, Daisho Ikeda, Hiroshi Ito, Akira Iwasaki, S. Jeong, HM Jeong, CH Jui, K. Kadota, F. Kakimoto, OE Kalashev, K. Kasahara, K. Kawata, I. Kharuk, E. Kido, SW Kim, HB Kim, JH Kim, JH Kim, I. Komae, Y. Kubota, MY Kuznetsov, KH Lee, BK Rubsandrjiev, JP Lundquist, JN Matthews, S. Nagataki, T. nakamara, A. Nakazawa, T. Nonaka, S. Ogio, M. Ono, H. Oshima, IH Park. , M. Potts, S. Pushilkov, JR Remington, DC Rodriguez, C. Lott, GI Rubtsov, D. Liu, H. Sagawa, N. Sakaki, T. Sako, N. Sakurai, H. Shin, JD Smith, P Sokolsky, BT Stokes, TS Stroman, K. Takahashi, M. Takeda, A. Takeda, Y. Tameda, S. Thomas, GB Thomson, PG Tyniakov, I. Tkachev, T. Tomita, SV Troitsky, Y. Tsunesada, S. Udo, FR Urban, T. Wong, K. Yamazaki, Y. Yuma, YV Zeser, Z. Zunder, November 23, 2023. science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.abo5095
Source: scitechdaily.com