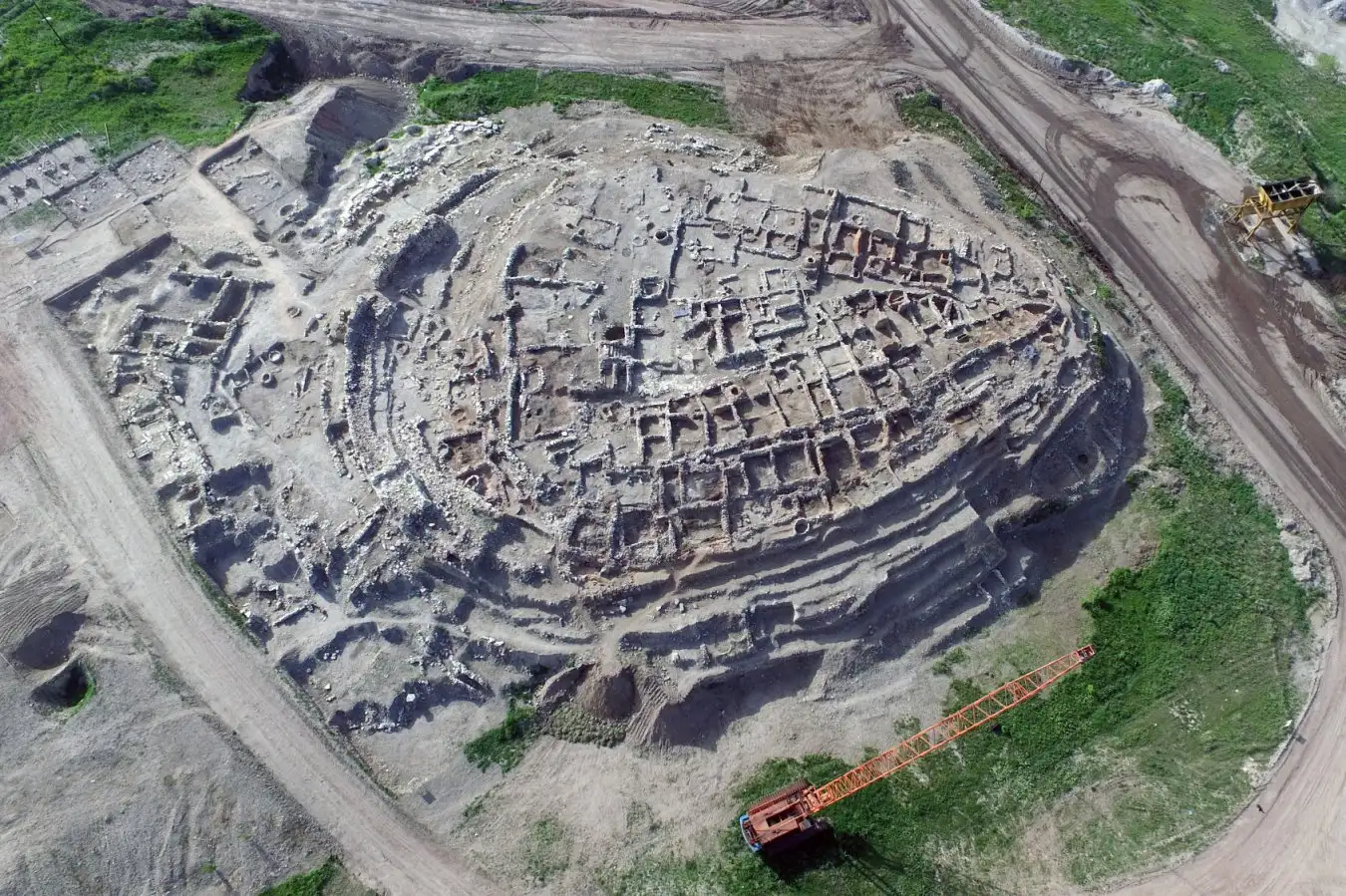
The remnants of Seyitömer Höyük in western Turkey exemplify a classic Luwian settlement.
Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism, General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums, Department of Excavations; Luwian Studies #0255
Surveys of archaeological locations in western Turkey have uncovered numerous significant towns that thrived during the Bronze Age. This lends credence to the contentious theory that this area hosted influential political entities which contributed to the upheaval in the eastern Mediterranean around 3,200 years ago.
Historically, scholars have recognized several prominent Bronze Age civilizations coexisting in the Eastern Mediterranean from approximately 2000 to 1200 BC, including the ancient Egyptians, the Mycenaean Greeks, and the Hittites of present-day central Turkey.
Yet, President Eberhard Sanger, Luwian research, has long thought that critical elements might be missing from the current understanding. He theorizes that there existed a number of formidable states in western Turkey, positioned between the Hittites on the eastern side and the Mycenaeans on the western side.
A decade ago, Sanger revealed findings based on satellite imagery suggesting that western Turkey was home to archaeological sites supporting his theory. However, the timelines of occupation at these locations remained unclear from the images alone.
In the ensuing years, Sanger and his team have analyzed excavation reports from various Turkish sites and personally visited many locations to deepen their knowledge of their historical context.
The focus has been on large sites exceeding 100 meters in diameter, where archaeologists uncovered Bronze Age pottery. The newly published database catalogs 483 archaeological sites across western Turkey fulfilling these criteria. “We are studying settlements that hosted hundreds of individuals over centuries,” Sanger noted.
He speculates that these settlements were organized into a network of small states, which he collectively refers to as the Ruwian states. This evokes parallels to Mycenaean civilization, which also appeared to be comprised of several small states, each with its respective palace and king. Sanger remarked that these provinces remain largely unrecognized due to the tendency of Turkish excavators to focus on individual site contexts rather than regional interactions.
The notion that a small yet significant state existed in this region isn’t entirely inconsistent with current evidence. “There was a substantial kingdom known as Arzawa in western Anatolia,” states Guy Middleton from Newcastle University, UK, who did not participate in the study. “The king of Arzawa communicated with the pharaoh.” [Amenhotep III] During a period when the neighboring Hittite kingdom was waning, he was referred to as the “Great King,” akin to one of the gangsters.
However, much archaeological evidence pertaining to Arzawa and additional Ruwian provinces remains elusive, according to Sanger. He attributes this partly to the fact that many sites associated with these states experienced continued occupation well after the Bronze Age, effectively burying the Ruwian layers under more recent archaeological layers. “It can take years or even decades of excavation to reach Bronze Age strata,” he remarked.
Ian Rutherford, a researcher from the University of Reading in Britain, states that “Luwian” was a term used by the Hittites to refer to the people of western Anatolia, but without additional evidence, it’s challenging to ascertain if everyone there was Luwian or if non-Luwian cultures were also present. “I remain skeptical,” he commented.
Most provocatively, Sanger posits that the Luwian states occasionally formed extensive political coalitions that could contend with the more recognized Bronze Age civilizations of the Eastern Mediterranean. He even suspects that a Luwian confederacy played a role in the collapse of Hittite civilization approximately 3,200 years ago, instigating an assault on ancient Egypt at that time. A mysterious group known as the Sea Peoples often features in these historical events, and Sanger believes they were Luwians. Many researchers, including Middleton, contend that the narrative surrounding the collapse of the Sea Peoples and Bronze Age civilizations is considerably more intricate and nuanced.
Nevertheless, Sanger finds support for his theories in unexpected sources. One such source is the myth of the Trojan War in ancient Greece, set during the late Bronze Age. In this narrative, vast numbers of Mycenaean Greeks purportedly engaged in a protracted ten-year conflict at Troy, which Sanger identifies as one of the proposed Luwian states.
He points out that the account appears odd, given that it reportedly took ten years for such a large Greek army to seize a relatively modest city. He theorizes that the tale gained traction in the centuries following the Bronze Age as audiences at that time interpreted it to depict a significant clash between the Greeks and a robust coalition of warriors from various Luwian provinces. “Fiction must resonate,” remarks Sanger.
Experience an unforgettable adventure through Cairo and Alexandria, two of Egypt’s most famed cities, where ancient history intertwines with contemporary allure. topic:
Cairo and Alexandria, pioneers of science in the ancient world: Egypt
Source: www.newscientist.com