As California prepares for another strong atmospheric river storm on Sunday, Lake Tulare serves as a reminder of the impactful effects these extreme storms can have.
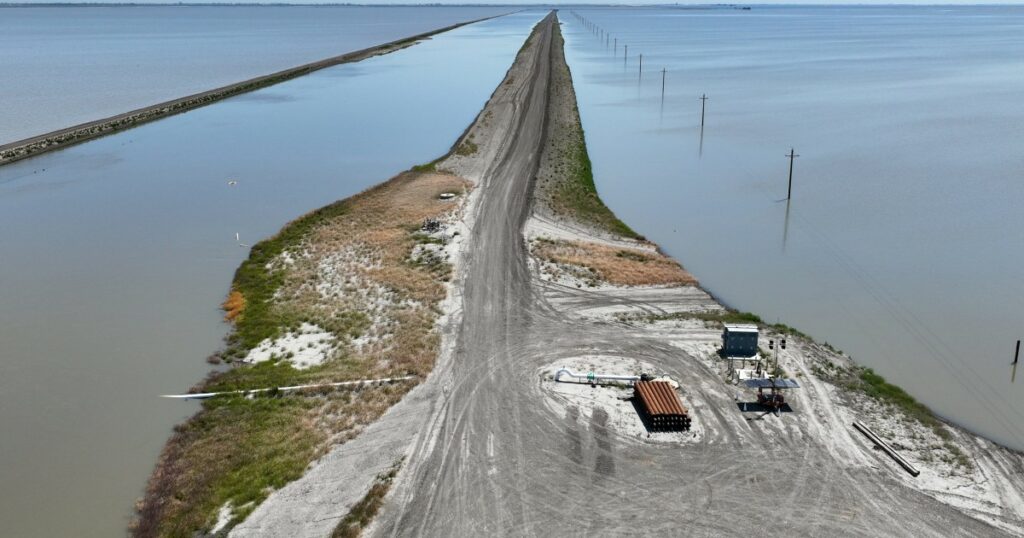
The lake’s floodwaters, which were formed after approximately 12 atmospheric river storms hit California in 2023, are still present 9 months after the resurgence of the “ghost lake.” More than a month later, they still cover thousands of acres of prime farmland.
This summer, the stagnant water of the lake became a gathering place for wild birds and caused an outbreak of avian botulism. Wildlife officials had to patrol daily by airboat and collect hundreds of dead birds. Submerged flooded vehicles and communication equipment at the bottom of the lake left farmers unable to access their fields.
The continuing presence of the lake in this part of the Central Valley emphasizes how the environmental impacts of last year’s extreme rainfall are still affecting California. While this weekend’s storms could bring heavy precipitation to other parts of the state, most flooding effects are not expected to last long.
Currently, Lake Tulare is rapidly shrinking despite recent rainfall. As of Thursday, about 4,532 acres of farmland were still underwater, but the floodwaters have subsided, according to Kings County spokesman Justin Caporusso. This means the lake is now less than 20 times smaller than last year’s peak, and life is returning to normal for nearby residents.
Sgt. Nate Ferrier of the Kings County Sheriff’s Office, who visited the lake in late January, noted that much of the lake has been cleaned up.
“The farming community was already revitalized,” he said. “There were tractors everywhere.”
The lake was a natural feature of the southern San Joaquin Valley until settlers dug irrigation canals to reroute water and drain agricultural land more than a century ago. Last year, the Tulare Basin flooded after a series of storms because reservoirs could not handle heavy snowmelt runoff from the Sierra Nevada mountains.
Caporusso stated that this week’s atmospheric river storms, expected to be accompanied by a significant storm on Sunday, are unlikely to have a significant impact on Tulare Lake. The reservoir upstream of the lake has the capacity to handle the precipitation, and the California Department of Water Resources found that about 45% of normal snow falls in the southern Sierra Nevada during this period.
Source: www.nbcnews.com