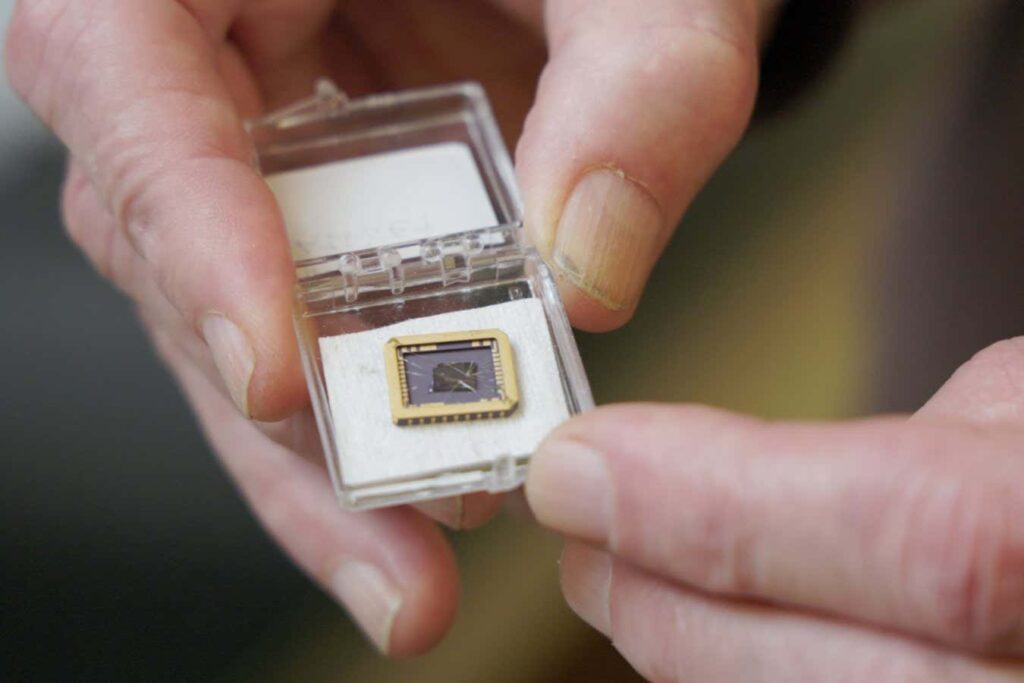
The team's graphene device grown on a silicon carbide substrate chip
Georgia Tech
A functioning, scalable semiconductor has been created from graphene for the first time, potentially paving the way for new types of computers that are faster and more efficient than today's silicon chips.
Graphene is a material made from a single layer of carbon atoms that is stronger than an equivalent thickness of steel. It is an excellent conductor of electricity and has excellent resistance to heat and acids. But despite its benefits, practical graphene semiconductors that can be controlled to conduct or insulate electricity at will have eluded scientists. Such semiconductors are key to creating the logic chips that power computers.
The problem is the lack of something known as a bandgap. Semiconductors have higher and lower energy bands and points at which excited electrons can hop from one to the other, or band gaps. This effectively turns the flow of current on and off, making it conductive or non-conducting, creating the binary number system of zeros and ones used in digital computers.
Previous research has shown that graphene can be made to behave like a semiconductor on small scales, but it has never been scaled up to a size that could be used in computer chips. Previous research has shown that wrinkles, domes, and holes in graphene sheets can have unusual effects on the flow of electricity, and that creating the right conditions for defects could lead to the creation of logical chips. It is shown. But so far nothing has scaled up.
now, Walter de Heer His colleagues at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta created graphene with a bandgap and demonstrated its operation as a transistor, an on/off switch that prevents or allows current to flow. Their process relies on technology similar to that used to create silicon chips, which should make it even more useful for scaling up.
De Heer's group used heated silicon carbide wafers to force the silicon to evaporate before the carbon, effectively leaving a layer of graphene on top. At the time of writing, Mr. de Heer was not available for an interview. said in a statement The electrical properties of graphene semiconductors were much better than those of silicon chips. “It's like driving on a gravel road versus driving on a highway,” he said.
Silicon chips are cheap to manufacture and supported by huge manufacturing infrastructures around the world, but we are reaching the limits of what these chips can do. Moore's Law states that the number of transistors in a circuit doubles approximately every two years, but the rate of miniaturization has slowed in recent years as circuit densities have been reached where engineers cannot reliably control the electrons. are doing. Graphene circuits have the potential to reignite progress, but hurdles remain.
“The fact that we're using wafers is important because it's really scalable,” he says. david carey At the University of Surrey, UK. “We can scale up this process using all the technologies that the entire semiconductor industry is familiar with.”
But Carey is skeptical that this development means the world will soon move from silicon to graphene chips. That's because new research requires many improvements in transistor size, quality, and manufacturing technology, and silicon has a huge head start.
“Most people who work in silicon research are exposed every day to new amazing materials that are trying to replace silicon, and nothing like this has ever happened before,” he says. . “If you're a silicon enthusiast, you'll be sitting pretty happily on top of the mountain. The idea of replacing your laptop with graphene isn't quite there yet.”
topic:
Source: www.newscientist.com