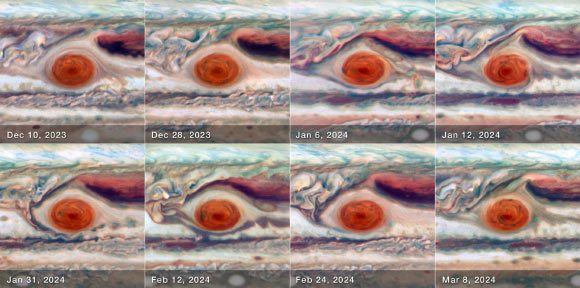
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope detected Jupiter’s most distinctive feature, the Great Red Spot, on eight dates over a single 90-day oscillation period from December 2023 to March 2024. I observed it.
simon others. measured the size, shape, brightness, color, and vorticity of the Great Red Spot over one complete oscillation cycle. Image credit: NASA/ESA/Amy Simon, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center/Joseph DePasquale, STScI.
“We knew its motion varied slightly with longitude, but we didn’t expect it to oscillate in magnitude,” said Dr. Amy Simon, an astronomer at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
“As far as we know, it has never been identified before.”
“This is really the first time we’ve had a proper imaging rhythm for the Great Red Spot.”
“Using Hubble’s high resolution, we can say that the Great Red Spot is steadily moving in and out at the same time as it moves faster and slower.”
“This was very unexpected. There is no hydrodynamic explanation at this time.”
Dr. Simon and colleagues used Hubble to zoom in on the Great Red Spot and closely observe its size, shape, and subtle color changes.
“If you look closely, you can see that many things are changing every day,” Dr. Simon said.
“This includes ultraviolet observations showing that the clear center of the storm is brightest when the Great Red Spot is at its maximum magnitude during its oscillation period.”
“This indicates less absorption of haze in the upper atmosphere.”
“As the Great Red Spot accelerates and decelerates, it’s working against the jet stream, which has strong north and south winds,” said Dr. Mike Wong, an astronomer at the University of California, Berkeley.
“It’s similar to how having too many ingredients in the middle of a sandwich forces a slice of bread to expand.”
The authors contrasted this with Neptune. On Neptune, dark spots can drift violently within their latitudes without a strong jet stream to hold them in place.
The Great Red Spot is held at southern latitudes trapped between the jet stream, with limited telescopic observations of Earth.
Astronomers predict that the star will continue to shrink and then assume a stable, less elongated shape.
“Currently, we’re overfilling that latitudinal band compared to wind fields,” Dr. Simon said.
“Once it contracts within that band, the wind actually holds it in place.”
“We predict that the size of the Great Red Spot will probably stabilize, but so far Hubble has only observed it for one oscillation period.”
team’s result Published in Planetary Science Journal.
_____
Amy A. Simon others. 2024. A detailed study of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot over a 90-day oscillation period. planet. Science. J 5,223;doi: 10.3847/PSJ/ad71d1
Source: www.sci.news