A team of Chinese scientists has assembled a reference genome from telomere to telomere. Korean ginseng (Korean ginseng)A representative of traditional Chinese medicine.
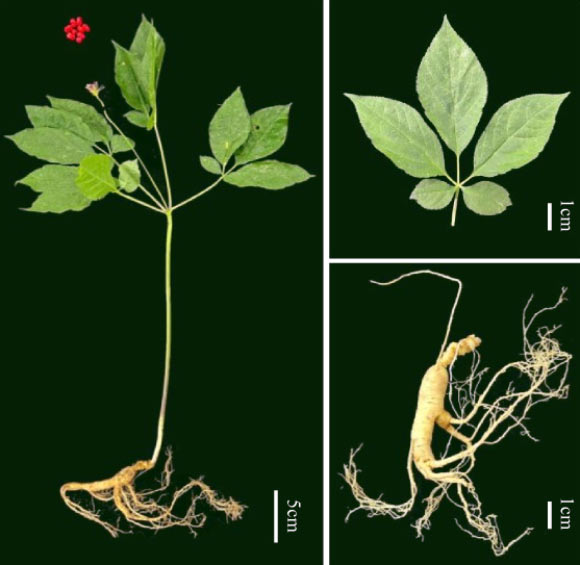
Overview of morphological characteristics of Korean ginseng (Korean ginseng). Image credit: Song others., doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae107.
Ginseng is one of the most important medicinal plants and is cultivated in Northeast Asia, including China, Korea, Siberia, and Japan, and in smaller quantities in North America.
As recorded in the ancient Chinese text Shennong Benmatao Jing, the perennial root of ginseng has been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine and as a functional food and beverage with bodily and immune-boosting properties.
Ginseng has a very long history of being collected from the wild in fields, and cultivation began about 500 years ago. Since then, selective breeding has begun and cultivated varieties have become common.
“Like other herbs, medicinal ginseng has complex metabolites that are believed to be active compounds, of which triterpene saponins (ginsenosides) are the most important class,” said Wei Li, PhD, of the Shenzhen Institute of Agricultural Genomics, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and colleagues.
“Ginseng probably contains more than 100 types of ginsenosides, but the synthesis pathways of most of the ginsenosides remain unknown.”
In the new study, Dr. Lee and his co-authors assembled a ginseng reference genome from telomere to telomere.
“We used this intertelomeric reference genome to study the phylogeny and evolution of ginseng and to explore the asymmetric loss and biased expression of genes among its subgenomes,” they explained.
The authors identified 77,266 protein-coding genes in the 3.45 Gb ginseng genome.
The team also identified asymmetric gene loss and biased gene expression across the subgenomes, tracing the divergence back approximately 6.07 million years.
Their analysis revealed extensive expansion of gene families related to saponin biosynthesis and highlighted the importance of specific gene duplications in enriching these pathways.
Comparative genomic analysis with related species will provide further insight into the evolutionary strategies employed by ginseng to maximize its medicinal properties.
“The complete sequencing of the ginseng genome is a monumental achievement in plant research,” Dr Lee said.
“Not only will it broaden our understanding of the genetic complexity of medicinal plants, but it will also introduce sophisticated methods for cultivating ginseng varieties with superior health properties.”
“Comprehensive sequencing of the ginseng genome has laid the foundation for precision breeding techniques aimed at enhancing its medicinal properties.”
“This research not only has immediate applications in the intensification of ginseng cultivation, but also serves as a model for studying other medicinal plants, potentially revolutionizing pharmacology and crop intensification strategies with natural products.”
of result Published in the journal Horticultural Research.
_____
Song Yi-ting others2024. Telomere-to-telomere reference genome Korean ginseng Our focus is on the evolution of saponin biosynthesis. Horticultural Research 11 (6): uhae107; doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae107
Source: www.sci.news