Experts caution that you might be unintentionally increasing your risk for a hereditary condition that leads to elevated cholesterol levels, according to new findings. Familial hypercholesterolemia can remain undetected for generations, thereby heightening the risk of heart attack and stroke for affected individuals, as reported.
This condition impacts approximately 1 in 200-250 individuals globally and leads to elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol from birth. LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because it contributes to arterial plaque buildup. However, researchers indicate it frequently goes unnoticed by standard testing methods.
To assess how many cases of familial hypercholesterolemia remain undiagnosed, Mayo Clinic researchers conducted an analysis involving 84,000 individuals. They specifically examined exome sequencing data, a genetic test that evaluates the segments of DNA that code for proteins.
Among these participants, 419 were identified as being at risk for familial hypercholesterolemia, with 90% unaware of their condition.
Adding to the concern, one in five of these individuals had already developed coronary artery disease.
The findings suggested that these patients would likely not be identified through standard genetic testing methods.
At present, genetic testing in the United States is only conducted on those exhibiting sufficiently high cholesterol levels or possessing a recorded family history of such levels—an issue identified by Mayo Clinic researchers as a “blind spot” in national guidelines. Seventy-five percent of those diagnosed in this study would not have qualified under these criteria.
The study emphasizes that regular screenings can reveal symptoms and potentially save lives, though other researchers highlight that this is not straightforward.
“The challenge is that screening everyone who would benefit from a genetic test can be prohibitively expensive, necessitating certain thresholds,” remarked cardiometabolic medicine researcher Professor Naveed Sattar in an interview with BBC Science Focus.
“Broadening screening efforts for familial hypercholesterolemia will only be feasible if testing costs decrease significantly. Nonetheless, we still need more individuals to undergo blood tests and seek genetic evaluations.”
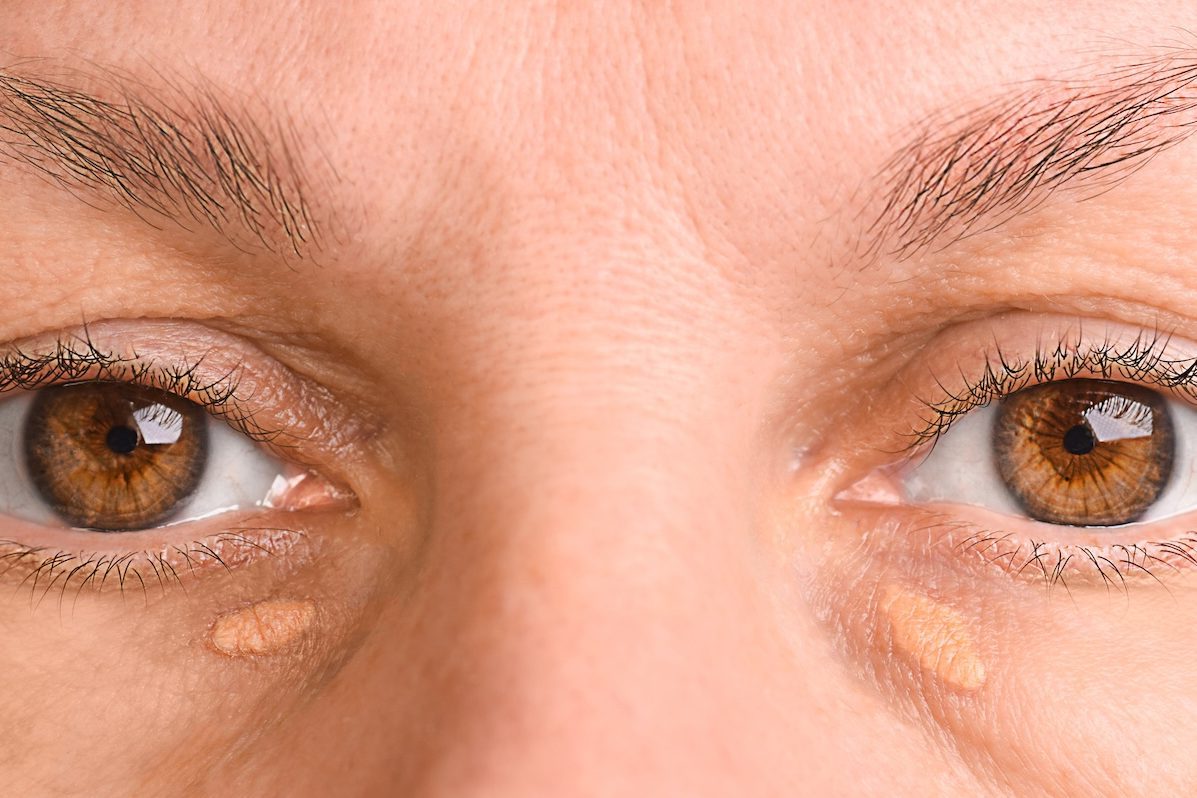
Most individuals with familial hypercholesterolemia exhibit no symptoms. However, Sattar points out that yellowish deposits beneath the skin or, if under 45, a grayish-white ring around the eye’s cornea can indicate the condition.
“Yet, many people have no visible signs. If there is a strong family history of early heart attacks—especially if a first-degree relative experienced one before age 50—you should consider getting a lipid test earlier than the typical midlife screening.”
The findings were published in the journal Circulation: Genomic Medicine and Precision Medicine.
Read more:
Source: www.sciencefocus.com